Obesity and tumor treatment new star target - GDF15-GFRAL
Growth differentiation factor 15 (Growth differentiation factor 15, GDF15), an endocrine hormone, is a member of the TGFβ superfamily, and plays an important role in the pathogenesis and mechanism of diseases such as obesity, diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver, and cancer. Enterprises focus on important targets. GDF15 is a secreted protein in the form of a 25 kDa dimer, which consists of two polypeptide chains containing 112 amino acids, and the single chains are connected by disulfide bonds.
In 2017, scientists from NGM Biopharmaceuticals and others discovered that GFRAL is the only receptor for GDF15. GDF15 acts by binding to GFRAL. After GFRAL binds to GDF15, it binds to the co-receptor RET to form a GDF15-GFRAL-RET complex, which activates the downstream AKT , ERK and PLC-ϒ signaling pathway.
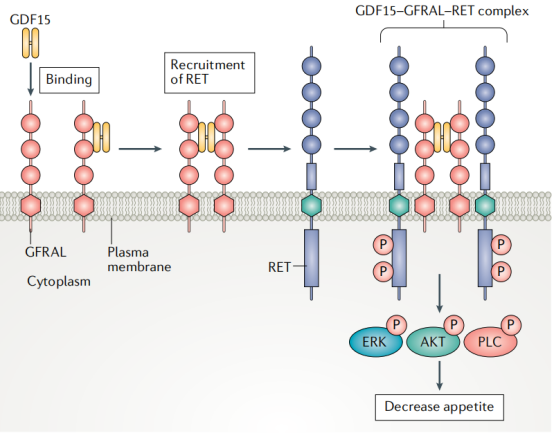
GDF15 expression and activation
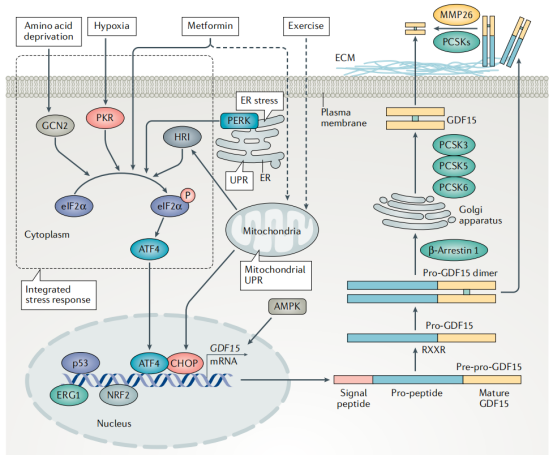
Under normal circumstances, GDF-15 is low expressed in most organs, but its expression is significantly increased in the placenta, and its expression is upregulated when organs such as liver, kidney, heart and lung are injured. Cellular stress, as well as metformin, leads to increased expression of GDF15, triggering various cancers, anorexia, weight loss, and metabolic changes.
GDF15 activation mode
One is ISR-induced GDF15 overexpression.
The second is that mitochondrial stress and UPR activate GDF15 overexpression.
Third, AMPK activation increases the expression of GDF15.
Fourth, metformin can promote the expression of GDF15 through PERK-ATF4-CHOP or mechanisms involving mitochondrial function.
GDF15 and GFRAL targets and diseases
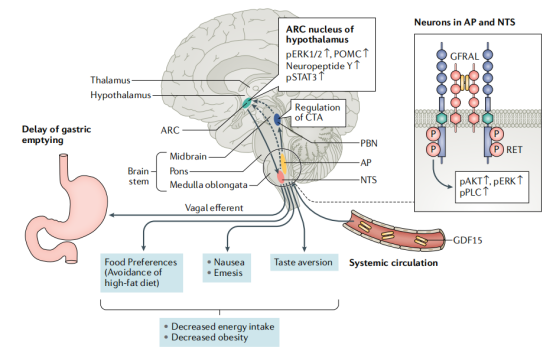
obesity-related diseases
GFRAL is predominantly present in neurons within the hindbrain-brainstem hindgut and nucleus propria, and elevation of GDF15 can lead to activation of GDF15-GFRAL-RET signaling in brainstem AP and NTS regions, projecting to PBN and ARC hypothalamic nuclei , regulates the activity of the vagal sympathetic nervous system, delays gastric emptying. Physiological levels of GDF15 also influence food preferences, limiting intake of high-fat diets. Therefore, GDF15 has become an important target for the treatment of obesity.
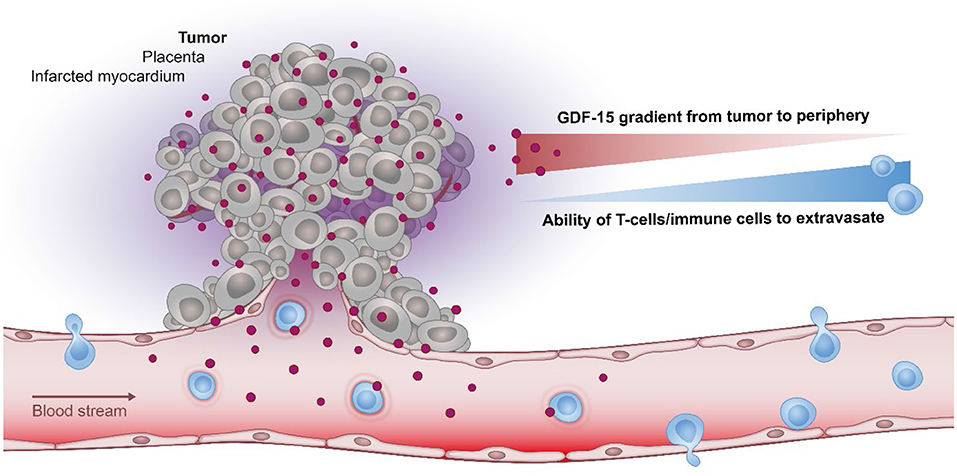
Cancer and related cachexia
Cancer-associated cachexia refers to uncontrollable weight loss in cancer patients during the course of the disease, and its symptoms include anorexia, weight loss due to loss of muscle mass and adipose tissue. In clinical practice, 50% to 80% of cancer patients will develop a complication called cachexia, which seriously affects the quality of life and clinical outcome of patients. Elevation of GDF15 is highly correlated with cancer-related cachexia and shortened cancer survival.
GDF15 has also been identified as a negative regulator of antitumor T cell activity, associated with suppressed immune responses and preventing T cell recruitment into the tumor microenvironment. At the same time, the tumor expresses and releases large amounts of GDF-15 in its microenvironment, which enables it to avoid recognition by circulating immune cells and mount an antitumor immune response. Therefore, inhibition of GDF15 is also an important target for overcoming resistance to standard cancer treatments and immunotherapies such as checkpoint inhibitors.
Drugs related to GDF-15 targets can treat tumors by: reducing the occurrence and development of cancer-related cachexia, improving cancer survival and quality of life; interfering with the activation and maturation of DC; reducing the induction of dendritic cells to T cells and Activation; blocking effective immune cell extravasation and tumor infiltration; inhibiting the killing effect of T cells and NK cells on tumor cells; inducing immunosuppression in tumor tissue by generating and enhancing the function of regulatory T cells.
In general, existing studies have shown that activating the GDF15-GFRAL signaling pathway can control food intake, thereby inhibiting the development of metabolic diseases and treating obesity-related diseases; inhibiting the GDF15-GFRAL signaling pathway can enhance the immune system’s killing of solid tumors, and can Treating or preventing cancer cachexia.
Current status of research and development of drugs targeting GDF15 and GFRAL
At present, several GDF15 and GFRAL target drugs are in the clinical research stage, and the indications are mostly focused on obesity, cancer and related cachexia, and positive clinical effects and progress have been achieved. Among them, the fastest-growing Visugromab (CTL-002) is a humanized GDF15 monoclonal antibody from CatalYm, Germany, which aims to neutralize GDF15 produced by tumors to counteract the immune suppression mechanism, enhance the infiltration of immune cells into tumors, and improve The activation of T cells by DC cells enhances the tumor-killing effect of T cells and NK cells, and has entered Phase 2 clinical research.
For the research and development needs of GDF15 and GFRAL target drugs, we have developed the hGDF/GFRAL&RET Effector Reporter Cell cell line, welcome to inquire. Part of the data is shown below:
hGDF/GFRAL&RET Effector Reporter Cell RQP74186
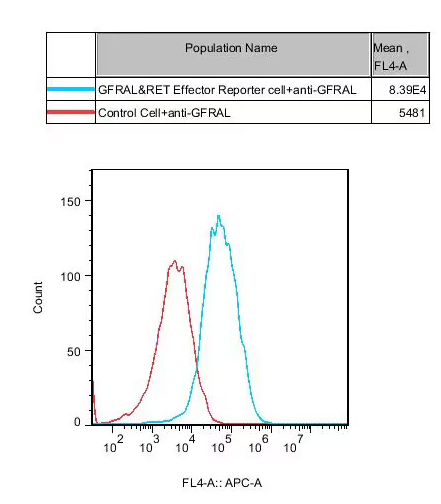
Figure 1. Recombinant hGDF/GFRAL&RET Effector Reporter Cell constitutively expressing GFRAL.
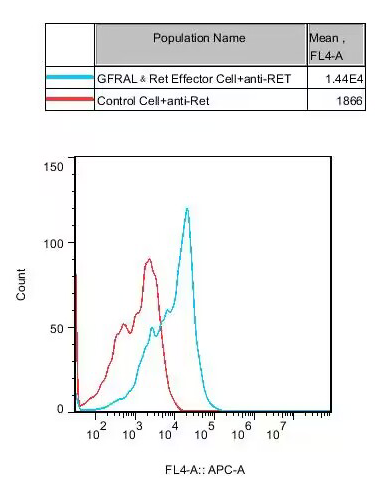
Figure 2. Recombinant hGDF/GFRAL&RET Effector Reporter Cell constitutively expressing RET.
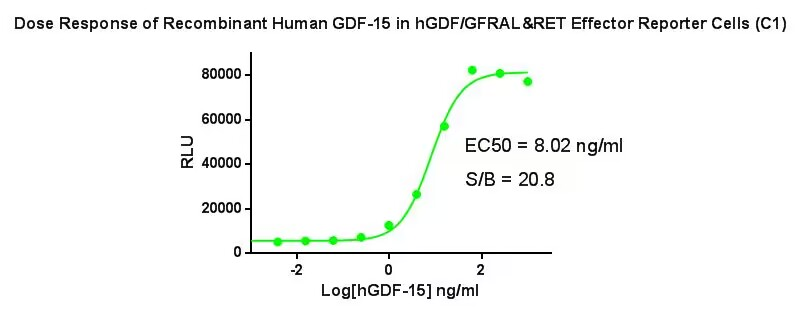
Figure 3. Dose Response of Recombinant Human GDF-15 in hGDF/GFRAL&RET Effector Reporter Cells (C1).
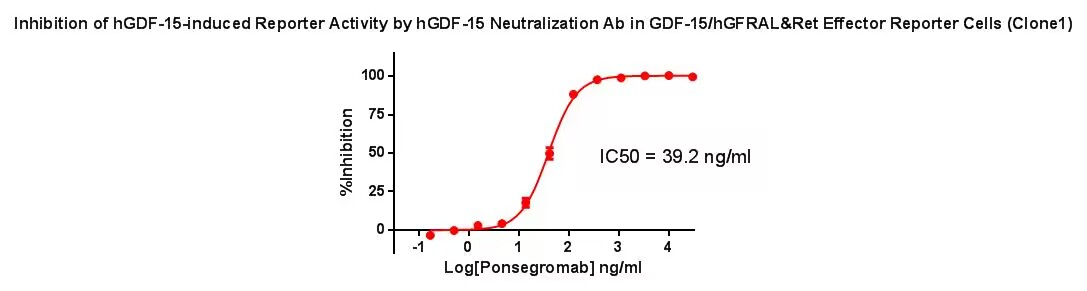
Figure 4. Inhibition of hGDF-15-induced Reporter Activity by hGDF-15 Neutralization Ab in GDF-15/hGFRAL&Ret Effector Reporter Cell (Clone1).

