OX40 & PD-1/L1 dual-immun examination point cell screening model
Although the immunotherapy based on immune examination points has achieved unprecedented success in the clinical treatment of some malignant tumors, most patients still have no response to these therapies, or they are durable quickly after a certain reaction at the initial stage. Although the procedural death -1 (PD-1) and the programmatic death ligand-1 (PD-L1) as the target, the inhibitor can restore the function of antigen-specific T cells to a certain extent, enhance the anti-antigen's specific T cells, and enhance the anti-antigen Tumor immunotherapy reactions, but still have limited efficacy in many clinical cases. In the body, antigen -specific T cells will be jointly regulated by co -suppression signals and common stimulus signals; therefore, theoretically blocking co -inhibitors and providing common stimulus signals to enhance T cell function may enhance the immune response of antitumor.
OX40 Introduction
OX40 (also known as CD134) is a common stimulating molecule expressed in the activated human T cell, which plays a role in T cell activation, amplification, differentiation, generating, and maintaining memory T cells. It belongs to the TNF receptor (TNFR) Super Family. The crystal structure of the molecule and its ligand complex (OX40L) is a trimer type composed of one trimer OX40L molecule and three OX40 monomers. Members of the family (TNFRSF) need to form a high -end multi -concentration structure like this to achieve sufficient downstream signal activation. Clinically, due to the lack of sufficient intensity activation, a single therapy of the excitement antibody usually shows a relatively weak curative effect. Therefore, the efficacy of the OX40 agonist antibody as a single therapy is very limited. Compared with the inspection point blocking antibodies, the combined antibody combination therapy of Anti-OX40+Anti-PD-1/L1 and anti-CTLA-4 shows a better anti-tumor effect. Therefore, the combination of OX40 agonist antibodies with immunotherapy against inhibitory receptors such as anti-PD-1/L1 is a very promising treatment strategy.
Research and development status
At present, some excitement anti -OX40 antibodies and other immunotherapy are combined with patients with malignant tumors and are in clinical trials. However, the combined treatment is not a simple 1+1. Both studies published by the Earle A. Chiles Institute and the Georgia Cancer Center show that simply the use of OX40 antibodies and PD-1 inhibitors to reduce the role of OX40 antibodies. And lead to poor tumor treatment of mice. According to some data of biological principles and clinical clinical, during combined treatment, OX40 targeted drugs should be treated with sequential treatment, and then PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors should be applied. In combined treatment, factors such as the combination method, the proportion of medication, the timing of administration, and order are all crucial. It also requires researchers to better understand the drug-resistant mechanism and immune dynamics of immunotherapy. Therefore, for OX40 and PD- 1/L1 The clinical design of the combination of medication points such as inhibitory immune checkpoints is relatively complicated and very challenging.
With the rapid development of double-specific antibody technology in recent years, this technology has also been applied to the development of dual-antidote for OX40 and PD-1/L1 at the same time. Compared with the combination of antibodies of PD-L1+OX40, PD- L1/OX40 bispecific antibodies can theoretically induce high-end OX40 to gather and achieve sufficient OX40 activation in a PD-L1 dependencies, thereby enhancing the effect of antitumor, and also reduced the complexity of clinical design in practical operations. In terms of function, PD-L1/OX40 double-specific antibodies play two aspects: 1) It will restore PD-L1 to restore antigen-specific T cell anti-tumor effects, and further enhance the Ax40 anti-Anti-mediated anti-anticipation of anti-anti-media Tumor reactions; 2) Compared with the anti-OX40 single drug, dual-resistance may reduce systemic toxicity and improve security due to its PD-L1 dependent OX40 activation. At present, a lot of pharmaceutical companies have deployed the development of PD-L1/OX40 dual anti-drugs. In February this year, Corning Jerer PD-L1/OX40 dual anti-KN052 new drug clinical trial application (IND) obtained the China National Drug Administration (NMPA ) Approval, conducting phase Ⅰ clinical research in China, and announced the completion of the first patient administration in June. This is the world's first PD-L1/OX40 dual resistance to the human clinical research stage; Mai Bio-targeted PD-L1/OX40 dual anti-EMB-09 was approved for clinical research in Australia; in addition, Cinda's PD-L1/OX40 dual anti-IBI327 was also in the pre-clinical stage, and as early as 2020 AACR disclosed Its preclinical research data.
For the research and development of PD-1/L1 & OX40 antibody drugs, especially the two-specific antibody drugs, we have specially developed PD-1/L1 & OX40 dual-target cell screening models, which can be measured and evaluated from cell horizontal functional PD-1/L1 & OX40 combination The efficacy, product information and related data of medication and bispecific antibodies are as follows: as follows:
PD-1/OX40 Dual Effector Reporter Cell RQP74163
PD-L1 aAPC Cell RQP74164
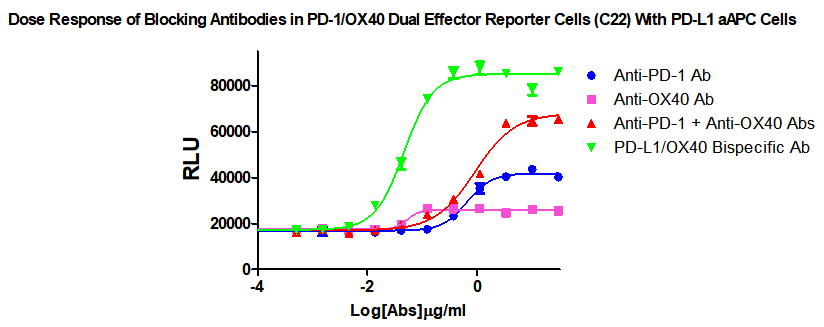
Figure 1. Dose Response of Blocking Antibodies in PD-1/OX40 Dual Effector Reporter Cells (C22) With PD-L1 aAPC Cells.

