A Novel Target of Tumor Immunity——Chemokine Receptor
Targets, such as PD-1, Tim-3, LAG-3, etc. However, with the serious homogenization competition and in-depth research, the pharmaceutical industry at home and abroad has gradually turned its attention to more aspects of innate immunity and the immune system, exploring more complex immune regulation mechanisms, and developing more abundant therapies. One type of target, chemokine receptors, is very worthy of attention. This type of target involves many aspects of the immune system, and its role and mechanism in tumor immunity is different from that of immune checkpoints, and great progress has been made. , has broad prospects.
Introduction to the Chemokine Receptor Family
Chemokines are a class of signaling proteins secreted by cells that induce the ability of adjacent responding cells to direct chemotaxis, and are named chemotactic cytokines. It plays an important role in inflammation, lymphoid organ development, cell trafficking, follicular form within lymphoid tissue, angiogenesis, and wound healing. At present, more than 50 chemokines have been found. Chemokine receptors are a class of GPCR proteins, which are expressed on the cell membranes of immune cells and endothelial cells, and are receptors that mediate the function of chemokines. According to the position of the disulfide bond in its natural ligand, chemokines are mainly divided into CC, CXC, CX3C, XC, and chemokine receptors are also divided into CCR, CXCR, CX3CR, and XCR. The following proteins: CCR1-10, CXCR1-7, CX3CR1 and XCR1.
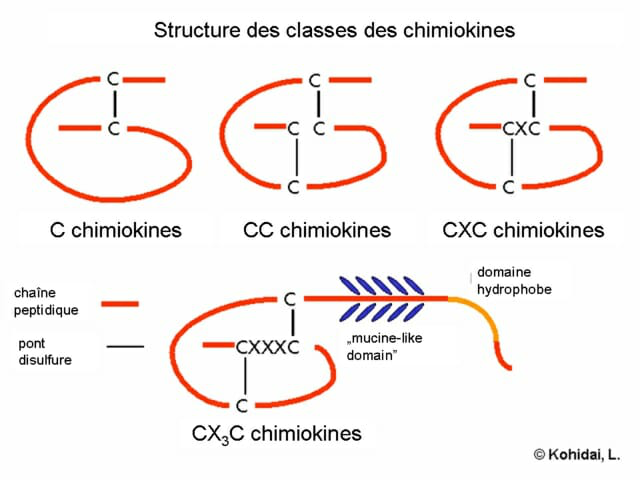
Chemokine receptors are widely expressed and distributed in the body, involving various organs and tissues such as the immune system and the nervous system. Among them, the distribution in the immune system is the most in-depth study. There are obvious differences in the expression of different receptors on different immune cells, the corresponding relationship between receptors and ligands is also crossed, and the entire regulatory network is very complex.
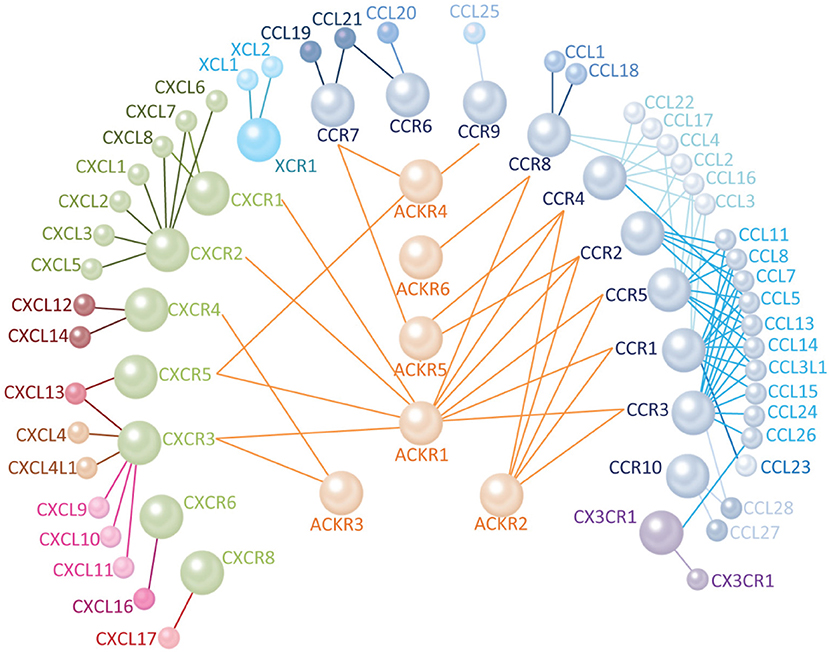
The interaction of chemokine receptors and their natural ligands is involved in the in vivo migration of various types of immune cells, thereby affecting the development and function of cells, including cell differentiation, anti-infection, inflammation, tumors, etc.
The relationship between chemokine receptors and tumors
Different chemokine receptors have different roles in tumors, and this difference is reflected in immune cell type and tumor type, which can be classified into several aspects:
1. Chemokine receptors are involved in the migration of killer immune cells. For example, CXCR3 is activated under the stimulation of chemokines such as CXCL9, and is involved in the migration of CD8+ T to cancer lesions such as ovarian cancer and rectal cancer, while CD8+ T moves to tumor tissue. of infiltration is highly correlated with patient survival.
2. Chemokine receptors are involved in the migration of inhibitory immune cells. For example, CXCR1/2 are involved in the migration of MDSCs to pancreatic cancer sites under the action of chemokines such as CXCL8. MDSCs are very important for the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.
3. Chemokine receptors are expressed on the surface of tumor cells, such as CCR5 is highly expressed on the surface of breast cancer, CXCR4 is highly expressed on the surface of more than 70% of cancer cells, etc. These receptors are directly involved in external signals on cancer cell proliferation, angiogenesis, Regulation of states such as migration.
4. The interaction of chemokine receptors and chemokine gins can induce lymphocyte migration and angiogenesis. For example, targeted inhibition of CXCR2 can inhibit CXCR2-promoted angiogenesis, improve tumor microenvironment, and promote T cell infiltration.
5. Chemokine receptors can promote tumor metastasis. For example, CXCR4 is highly expressed in some tumor cells, and by increasing CXCR4, tumors can be transferred to lymphocytes or tissues with high expression of CXCL12.
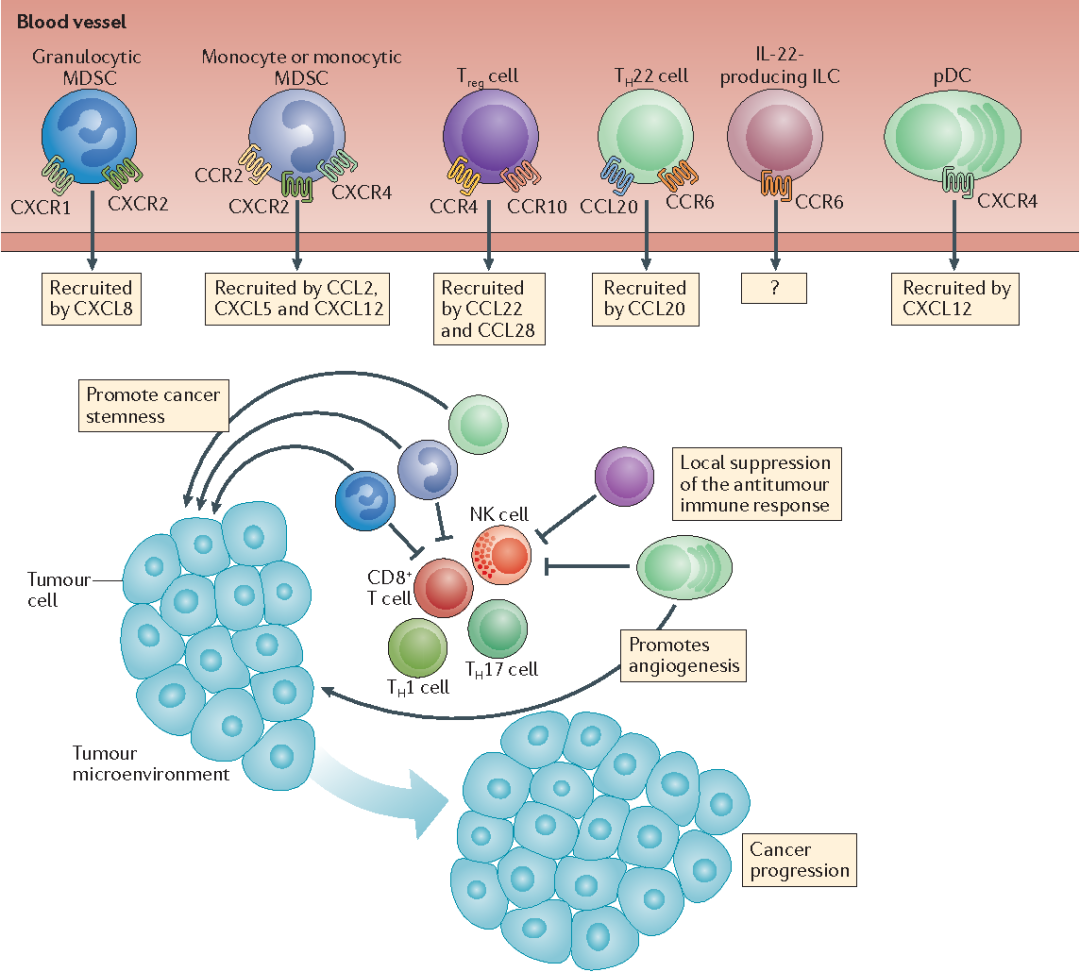
Fig 3. Chemokine receptors are involved in the interaction between immune cells and tumor cells
Current Situation of Chemokine Receptor Target Drug Development
Judging from the chemokine receptor drugs that have entered the clinic, the targets are concentrated on a few targets such as CCR2, CCR4, CCR5, CCR8, CXCR1, CXCR2, CXCR3, CXCR4, etc. The mechanism research of these targets is relatively clear, and the drug effects The mechanism and effect are relatively clear. To date, three drugs targeting this receptor family have entered the market: the antibody drug Mogamulizumab for lymphoma, the CCR5 antagonist maraviroc for HIV, and the CXCR4 antagonist plerixafor for hematological malignancies.
Mogamulizumab targeting CCR4 is the first approved antibody drug targeting GPCR proteins, approved in Japan in 2012 for the treatment of relapsed or refractory CCR4-positive adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma; 2018 , FDA-approved for the treatment of mycosis fungoides or Sézary syndrome, a CCR4-positive cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
The mechanism of CXCR4 in tumor immunity is relatively complex. Among the drugs targeting CXCR4, Balixafortide and BL-8040 are the fastest progressing drugs, both of which are cyclic peptide drugs and are already in phase III clinical trials. Balixafortide is currently in Phase III clinical trials for the treatment of HER2-breast cancer. BL-8040 is currently in Phase III clinical stage and has been shown to affect "cold" tumors in multiple modes of action, including immune cell migration, tumor infiltration by immune effector T cells, reduction of immune suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment ( such as MDSCs), making "cold" tumors (such as pancreatic cancer) "hot" (making them sensitive to immune checkpoint inhibitors and chemotherapy).
CXCR1/2 are highly expressed on the surface of neutrophils, MDSCs and other cells, and migrate and infiltrate into tumor tissues under the chemotaxis of CXCL8 and other chemokines. In terms of clinical trials, Merck's Navarixin is relatively powerful, and there is a phase II clinical trial underway, including the combination with Merck's own pembrolizumab, which is tried in a variety of advanced solid tumors. AstraZeneca's AZD5069 and Syntrix Biosystems' SX-682 are at an earlier stage, both trying to be used in combination with other types of drugs.
From the point of view of target mechanism, chemokine receptors belong to another type of immune system proteins closely related to cancer besides immune examination. The track of checkpoint inhibitors provides the possibility of finding a way out, and the clinical treatment of tumors is also expected to gain more means.
Chemokine receptor target drug screening cell model
In response to the needs of chemokine receptor target mechanism research and new drug development, Kebai Bio has launched a series of chemokine receptor target drug screening cell models. Some of the data are shown below. Welcome to inquire.
Partial product data
CCR1/CHO RQP71353
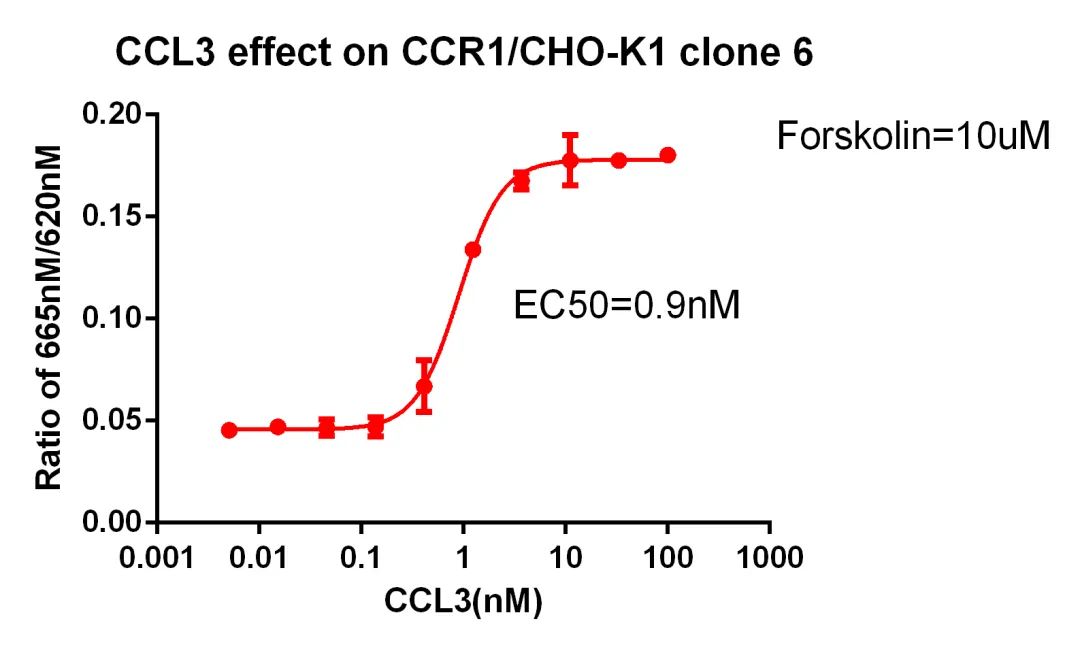
Figure 4. CCL3 effect on CCR1/CHO-K1 clone 6.
CCR10/CHO RQP71355
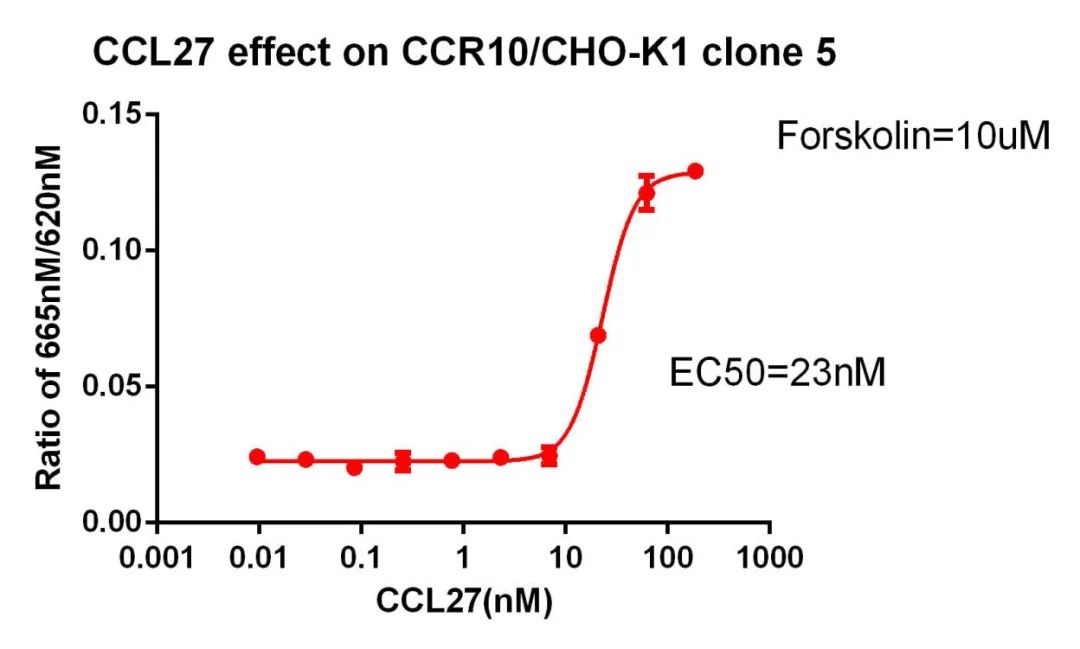
Figure 5. CCL27 effect on CCR10/CHO-K1 clone 5.
CCR2/CHO RQP71350
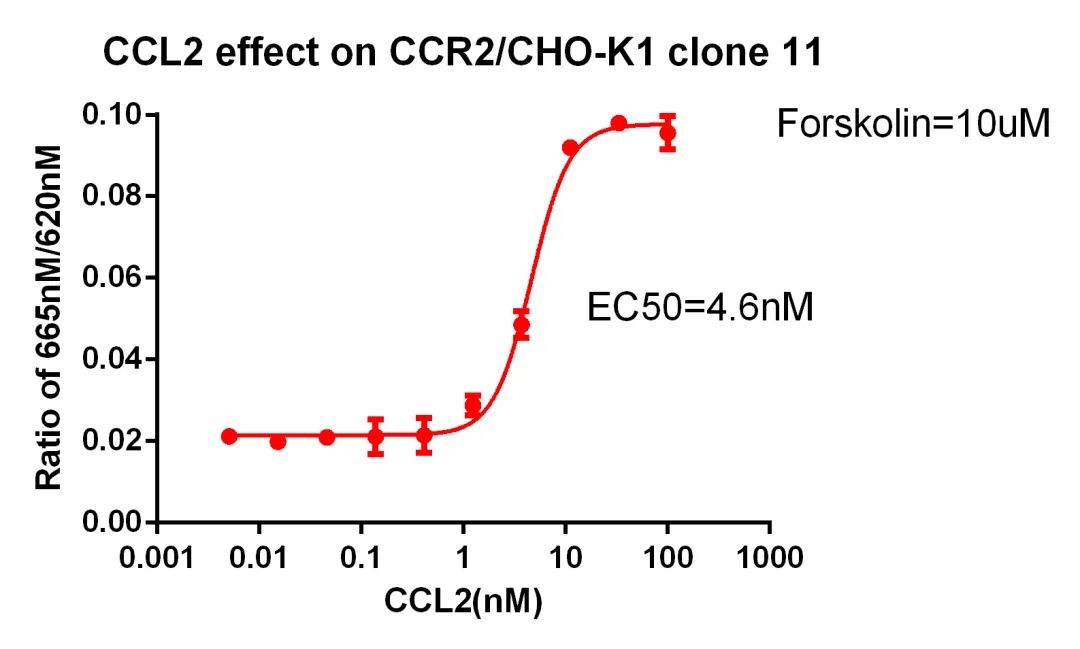
Figure 6. CCL2 effect on CCR2/CHO-K1 clone 11.
CCR4/β-Arrestin/CHO RQP71349
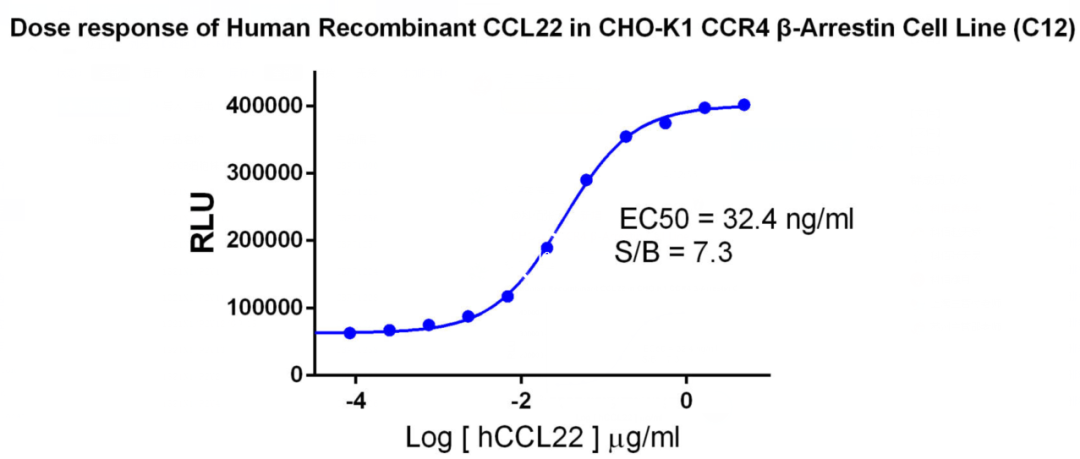
Figure 7. Dose response of Human Recombinant CCL22 in CHO-K1 CCR4 β-Arrestin Cell Line (C12).
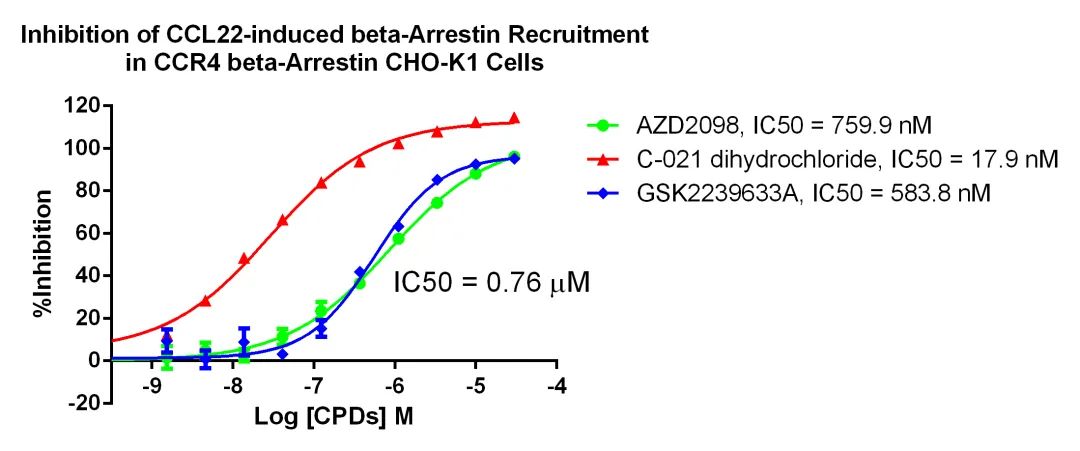
Figure 8. Inhibition of CCL22-induced beta-Arrestin Recruitment in CCR4 beta-Arrestin CHO-K1 Cells.
CCR5/CHO RQP71352
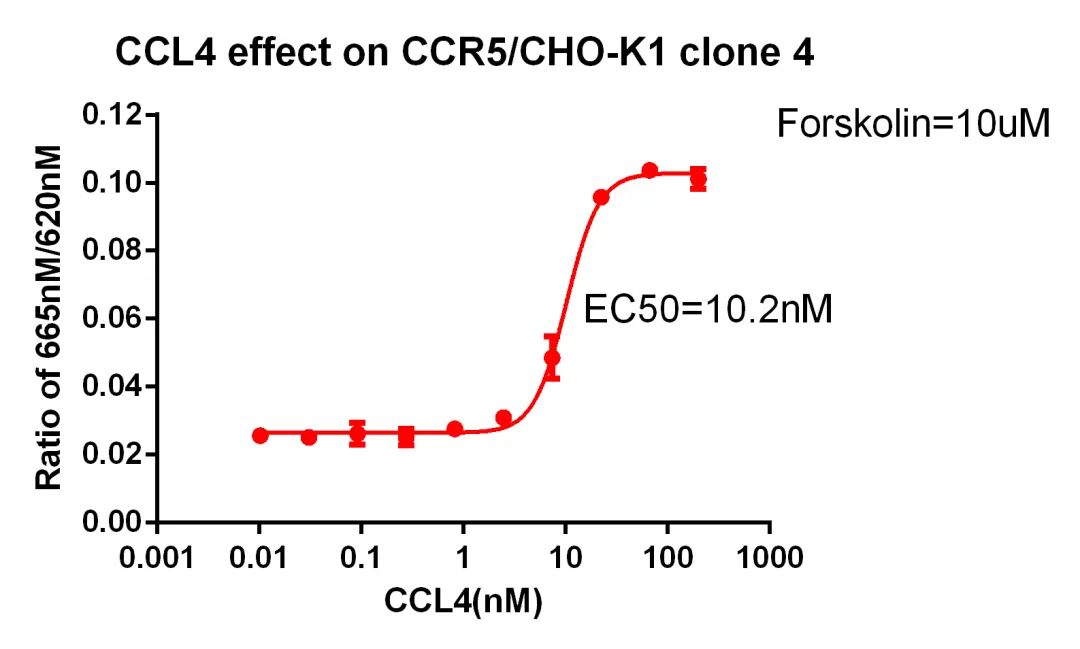
Figure 9. CCL4 effect on CCR5/CHO-K1 clone 4.
CCR5/Ga15/CHO RQP71057
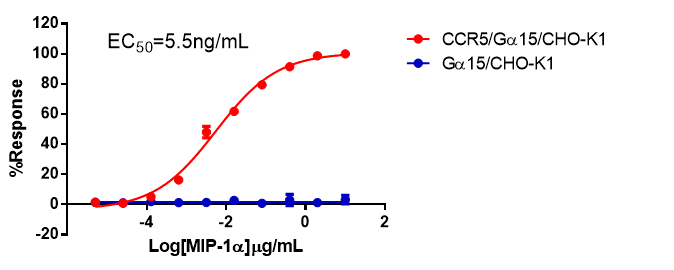
Figure 10. MIP-1α-induced concentration-dependent stimulation of intracellular calcium mobilization in CCR5/Gα15/CHO and Gα15/CHO cells.
CCR6/CHO RQP71354
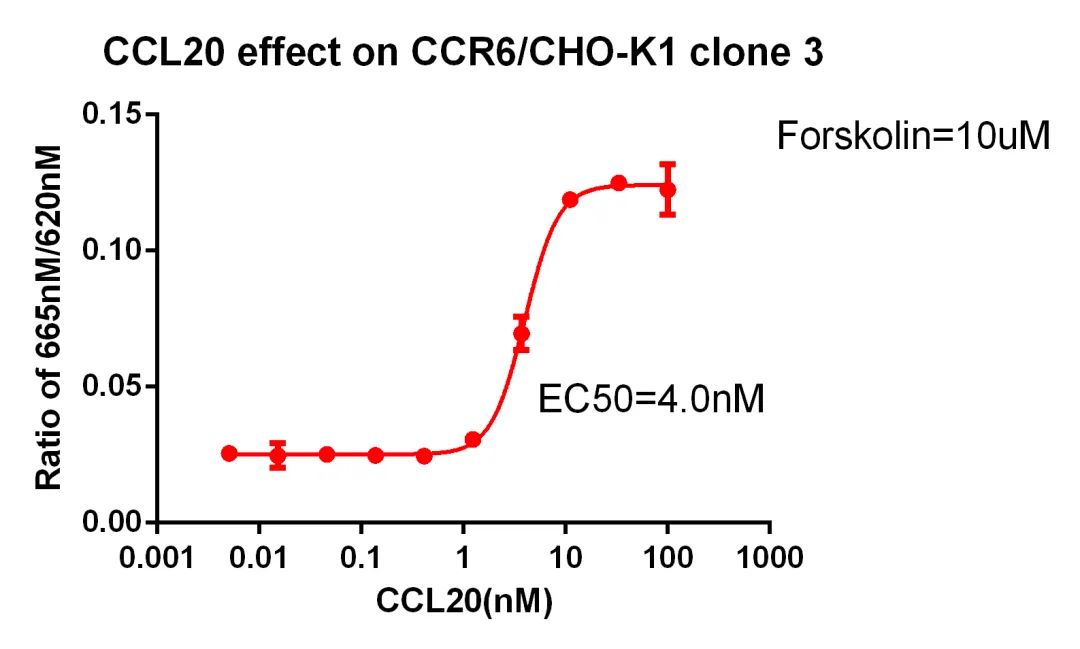
Figure 11. CCL20 effect on CCR6/CHO-K1 clone 3.
CCR7/CHO RQP71351
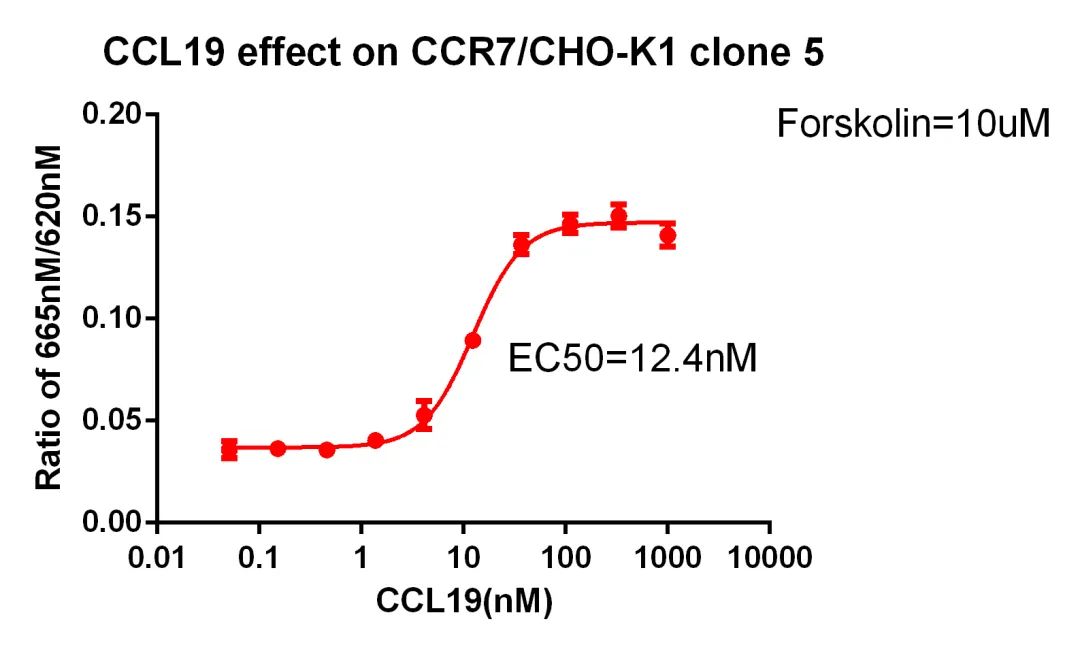
Figure 12. CCL19 effect on CCR7/CHO-K1 clone 5.
CCR8/CHO RQP71364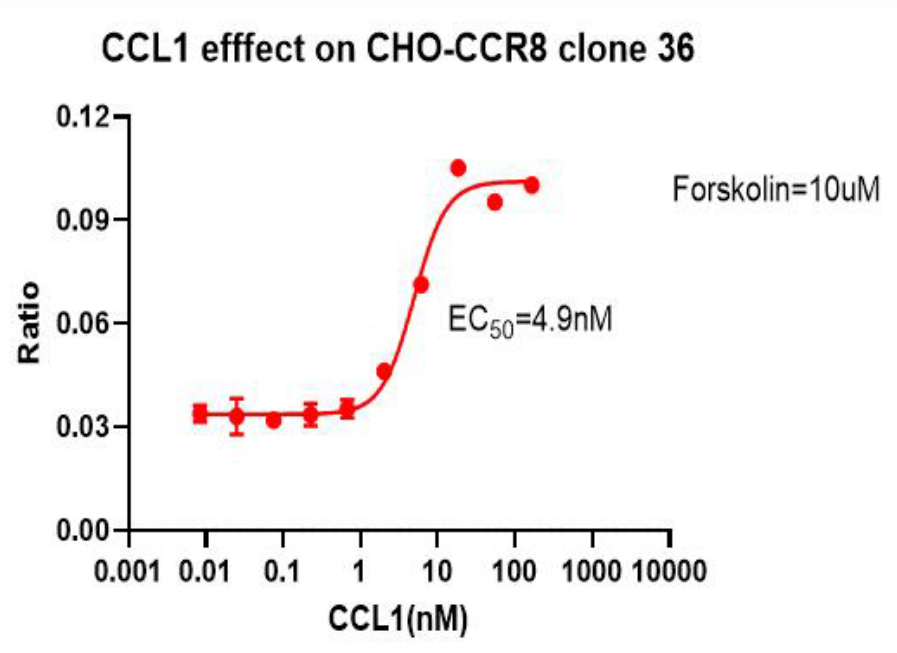
Figure 13. CCL1 effect on CCR8/CHO clone 36.
CCR8/β-Arrestin/CHO RQP71363
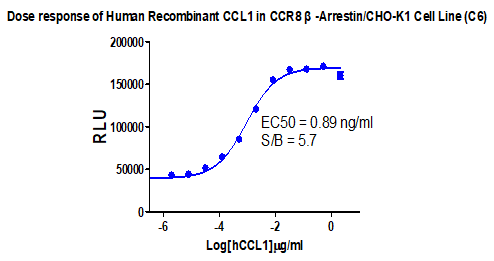
Figure 14. Dose response of Human Recombinant CCL1 in CCR8 β-Arrestin/CHO-K1 Cell Line (C6).
CXCR1/CHO RQP71360
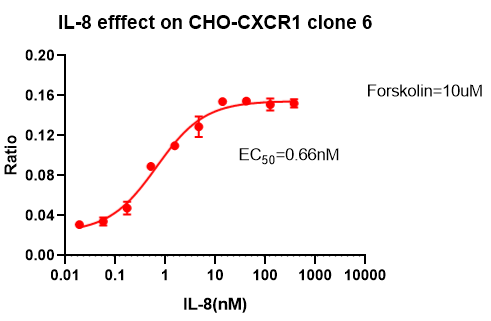
Figure 15. IL-8 efffect on CHO-CXCR1 clone 6.
CXCR2/CHO RQP71357
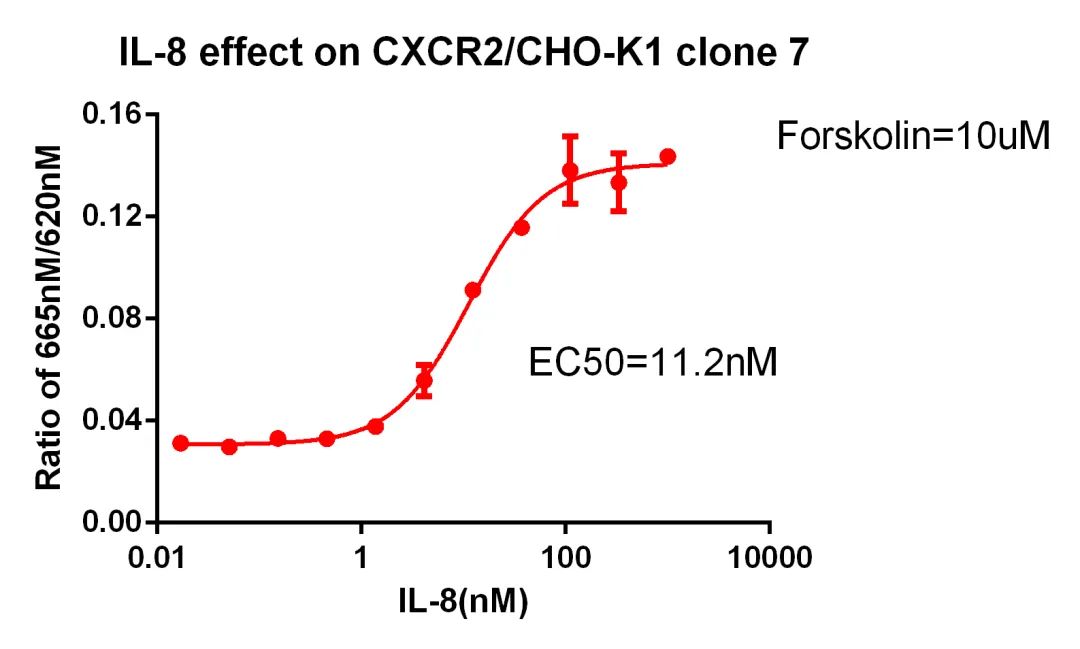
Figure 16. IL-8 effect on CXCR2/CHO-K1 clone 7.
CXCR3/CHO RQP71371
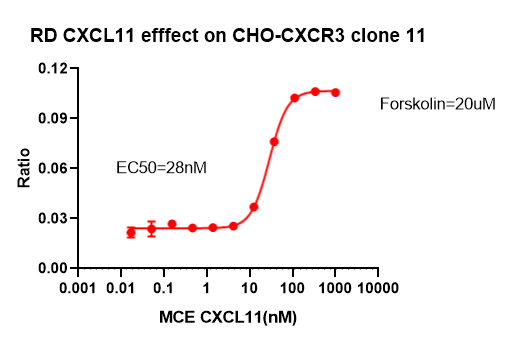
Figure 17. RD CXCL11 efffect on CHO-CXCR3 clone 11.
CXCR4/CHO RQP71358
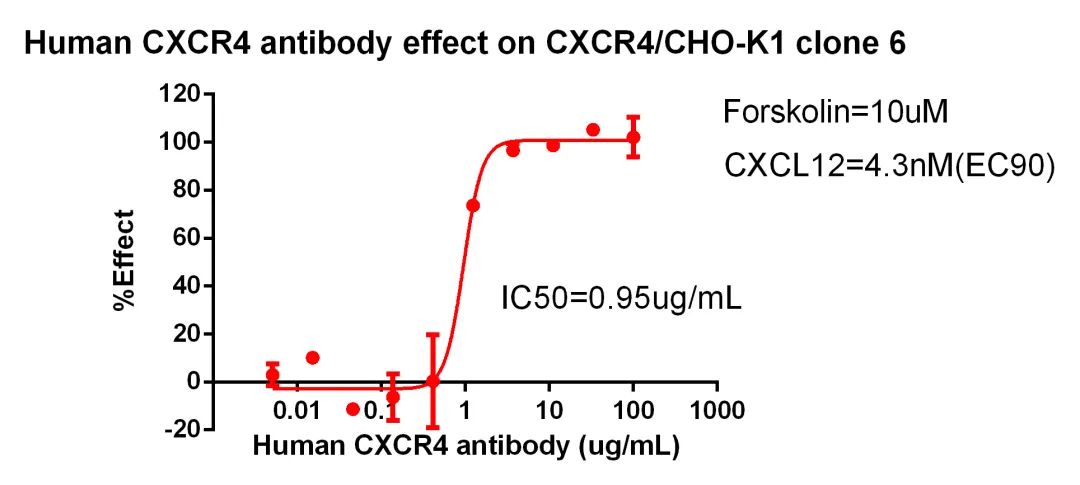
Figure 18. Human CXCR4 antibody effect on CXCR4/CHO-K1 clone 6.
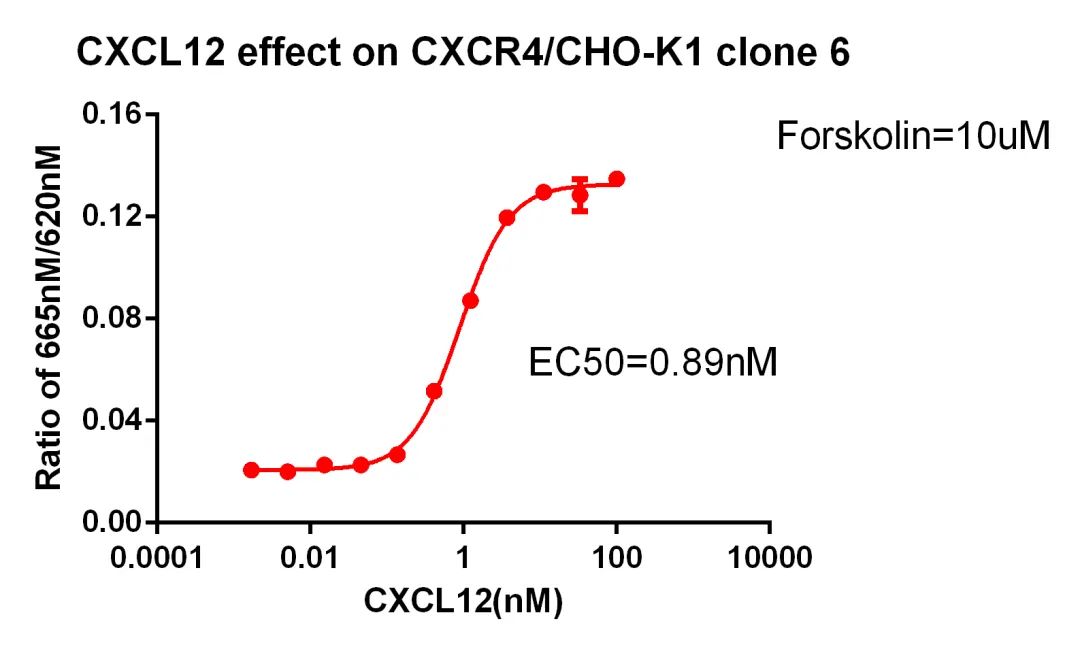
Figure 19. CXCL12 effect on CXCR4/CHO-K1 clone 6.
CXCR5/CHO RQP71370
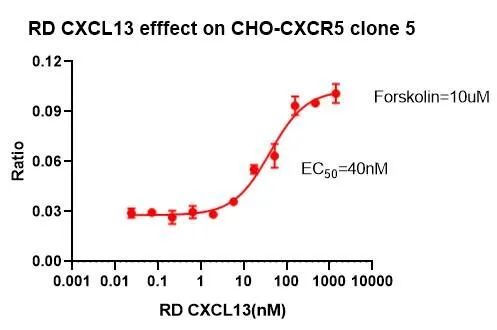
Figure 20. RD CXCL13 effect on CHO-CXCR5 clone 5.
CXCR6/CHO RQP71365
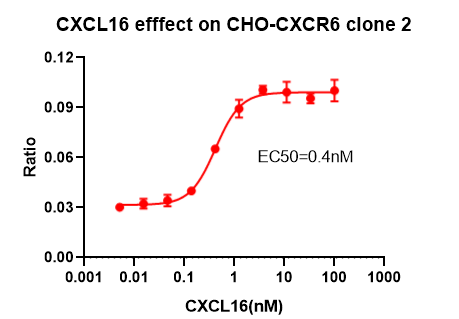
Figure 21. CXCL16 effect on CHO-CXCR6 clone 2.

