Have you participated in MRD testing for ctDNA?
MRD refers to residual tumor cells or markers in the body after treatment. There are usually three translations: Minimal Residual Disease, Measurable Residual Disease, and Molecular Residual Disease.
The term Minimal Residual Disease (Minimal Residual Disease) first appeared in hematological tumors, which means that the residual tumor cells after treatment are very small and very small, and the sensitivity of conventional detection is not enough to detect, generally due to drug non-response, drug resistance. Therefore, the detection of MRD at this time can be molecular detection (such as NGS) or surface marker detection (such as NGF). The detectable residual disease (Measurable Residual Disease) focuses on the angle of detection, and the research on residual disease is limited to the premise that it can be detected, and then the molecular residual disease (Molecular Residual Disease) mainly refers to molecular diagnosis that can detect tumors The residue, mainly through the detection of ctDNA, is suitable for hematological tumors and solid tumors at this time.
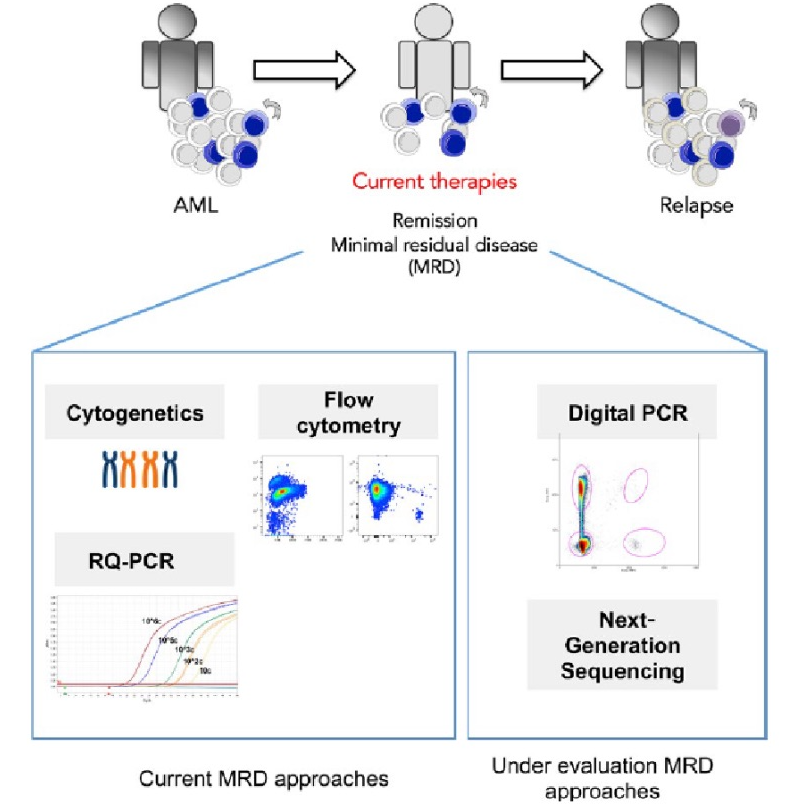
MRD is an important factor of tumor resistance and recurrence, and an important indicator of prognosis. In the 2021 version of the expert consensus on MRD testing for non-small cell lung cancer, there is a description: In a prospective multicenter study, a total of 101 patients with early breast cancer with somatic mutations were enrolled, and dPCR was used to dynamically track postoperative Plasma ctDNA, the results showed that ctDNA positivity was clearly associated with disease recurrence [hazard ratio HR=25.2, 95% confidence interval CI 6.7-95.6, p<0.001], and ctDNA predicted disease recurrence earlier than imaging, with a median of 10.7 months (95% CI 8.1-19.1 months). In another multicenter cohort study of 130 patients with stage II-III colon cancer, the ctDNA status of patients after radical resection was monitored by NGS captured by multiplex PCR, and the results suggested that patients with positive ctDNA 30 days after surgery had a much higher risk of recurrence than Negative patients (HR=17.5, 95% CI 5.4-56.4, p<0.001).
Current status of MDR detection of ctDNA
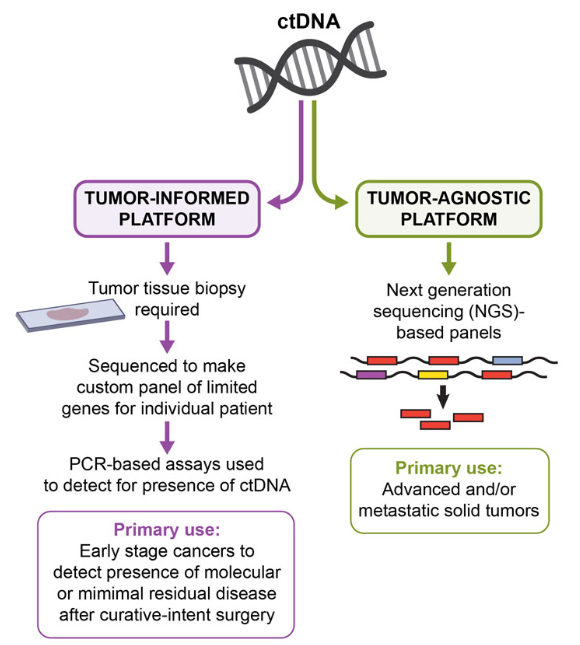
The existing MRD detection for ctDNA mainly has two technical routes: tumor-agnostic-assays (tumor-unknown analysis) and tumor-informed assays (tumor-informed/prior analysis), among which tumor-agnostic-assays is only for plasma detection, It uses fixed panels (usually driver genes and targeted drug genes, and also multi-omics methods) and analytical methods to detect and analyze ctDNA, representing the product Guardant Reveal of Guardant Health; tumor-informed assays need to be used for The primary tumor tissue is sequenced (usually WES) to identify the patient's specific genomic variation profile, and then a personalized panel is customized to test for ctDNA, which means that both tissue and plasma need to be tested. The representative product is Natera Signatera of the company. For the detection of MRD by domestic IVD companies, as of press time, the editor has encountered many tumor-informed assays.
One of the most difficult aspects of MRD technology is the detection ability and stability of ultra-low frequency mutations. Taking non-small cell lung cancer as an example, the median plasma concentration of cfDNA in early-stage NSCLC patients was 7.69 ng/mL, which was converted to 10 mL of plasma (20 mL Whole blood) contains about 20,000 haploid genomes (3.3 pg). Considering the loss of cfDNA library construction and the existence of at least 2 identical variant gene sequences, the limit molecular signal detected by ctDNA in 10 mL of plasma is 0.02%. . In addition, it is estimated from the TRACERx research data that in the case of a 1cm3 tumor volume, 10mL of plasma contains about 2 tumor-derived DNA molecules. Therefore, when performing MRD assays in NSCLC, the assay must be robust to ctDNA at ≥ 0.02% abundance. There is an important technical strategy here, that is, the strategy of Sample Level. For the site level of 0.02% or even lower, the sensitivity can be improved through the samples Level.
For the development of MRD diagnostic IVD for ctDNA detection, performance evaluation is indispensable, and naturally the development of standard products is also indispensable. We are a R&D and production enterprise focusing on diagnostic positive reference materials, detection limit reference materials, and precision reference materials in IVD research and development. , For the development of ultra-low frequency standard products of ctDNA, we plan to develop two types of products (Art-base and Nat-base), and hope to get more suggestions from industry experts.
The detection method for tumor-agnostic-assays mainly meets the needs of customized standards for different panels. Similar to the customization of liquid biopsy ctDNA standards, it is possible to develop a combination of panels for different cancer types. Here we tend to include small panels. A collection of differential loci of , medium panel, and large panel, and tend to be placed into pathogenic and suspected pathogenic loci to form a collection. The first problem to be solved is the calibration of ultra-low frequency mutations caused by ultra-low tumor proportions. We know that the detection limit of dPCR is generally 0.1%, and the frequency below 0.1% is generally difficult to distinguish from negative. Therefore, for ultra-low frequency mutations The detection of MRD sites is generally calibrated using ultra-deep NGS. Except for hematological tumors, there are currently no approved MRD detection kits for other tumors in China. In-depth NGS kits are used for calibration. There is no particularly good solution for this. Only in the dilution process of mixed samples, it can be as accurate and consistent as possible.
For the detection method of tumor-informed assays, according to the description of the process, the first choice is the development of customized standards. First, carry out WES detection on the sample tissue to be tested, and design a panel suitable for ultra-deep ctDNA detection according to the detection results, such as the capture method. , focusing on optimizing probe performance while developing corresponding standards for known mutations. Similarly, the problem of calibration of ultra-low frequency mutations caused by ultra-low tumor proportions will also be encountered. Here, we also hope to reach cooperation with companies that design and synthesize probes to complete the development and performance evaluation of panels within the limited time limit of recurrence monitoring.
Significance of MRD detection
The detection of MRD, the detection of ctDNA has demonstrated a clear clinical significance in the clinical monitoring of various tumor recurrences. There is an urgent need for MRD detection kits to help guide patients' adjuvant therapy and recurrence monitoring.

