GM-CSF, a new therapeutic target for cytokine storm and autoimmune inflammation
Cytokine stormsyndromes (CSS) are caused by a variety of cytokines in body fluids such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-17, G-CSF, GM-CSF, The rapid and massive production of MCP-1, IL-12, IFN-α, IFN-β, and IFN-γ is an important cause of acute respiratory distress syndrome and multiple organ failure. This is a systemic uncontrolled inflammatory response, often caused by microbial infection. When defending against pathogens, immune cells secrete a large number of cytokines, which in turn stimulate immune cells. Under normal circumstances, the inflammatory response will be regulated to a certain extent. However, in some cases, this regulatory mechanism fails, and the immune cells in the body are activated in large quantities, and the activated cells secrete more cytokines, resulting in a positive cycle and a cytokine storm. .
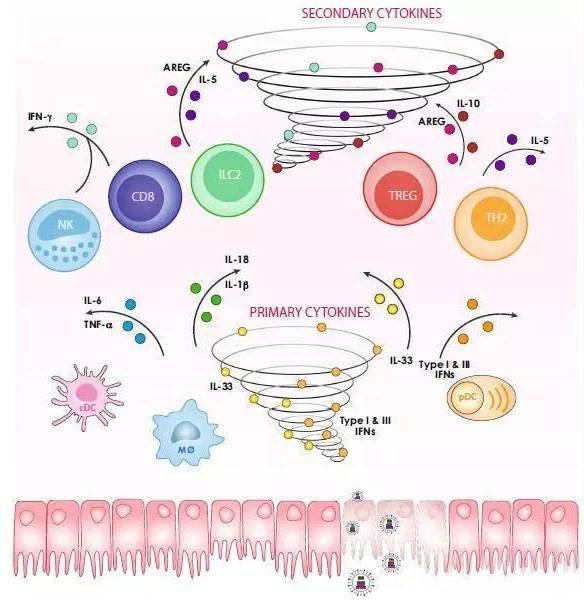
Fig 1. Cellular and molecular storm
Infections such as the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, influenza virus, and avian influenza virus can all cause cytokine storms, which are considered to be one of the important causes of death of patients. CAR-T cell therapy also releases a large amount of inflammatory cytokines, leading to cytokine storm and cytokine release syndrome, and IL-6 and GM-CSF are considered important targets for treatment.
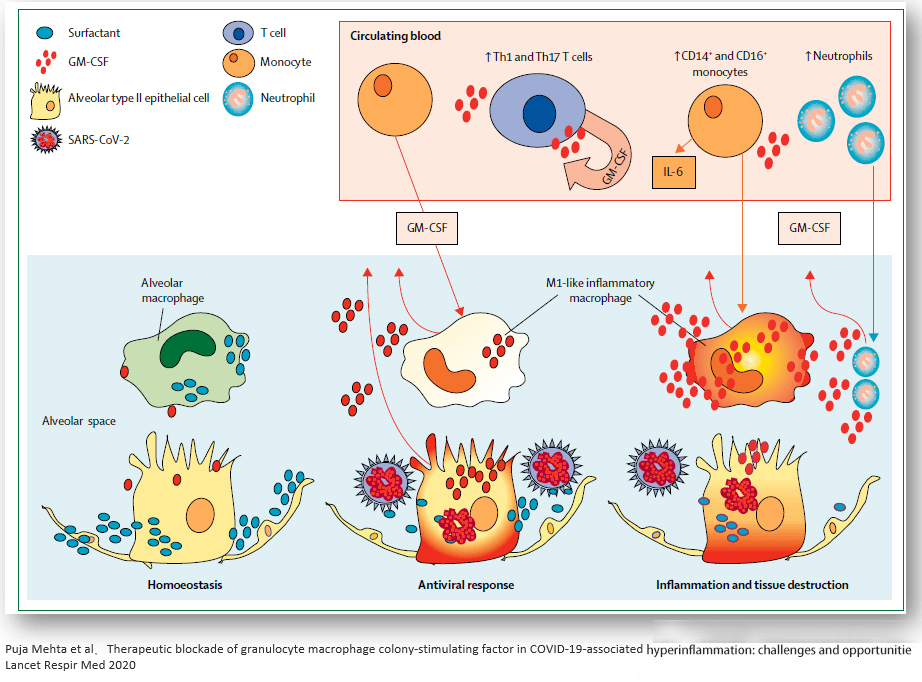
The mechanism of action of GM-CSF
GM-CSF (Granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor) is a secreted cytokine, expressed by a variety of cells, such as granulocytes, dendritic cells, T cells, B cells and so on. GM-CSF receptors are expressed in myeloid cells such as granulocytes and macrophages, and are composed of α and β chains. GM-CSF binds to the receptor to form a dodecameric complex, which activates the downstream JAK-STAT, PI3K, and NFκB pathways.
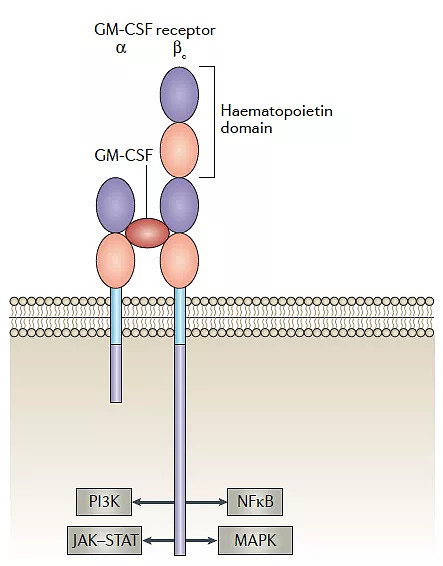
Fig 3. Mechanism of action of GM-CSF
GM-CSF Function
GM-CSF has a wide range of physiological functions, mainly promoting the generation, differentiation, activation, and survival of granulocytes and macrophages. And long-term maintenance, in the absence of GM-CSF, alveolar proteinopathy (PAP) occurs, and the function of pulmonary macrophages is defective, increasing the probability of pulmonary infection. The roles of GM-CSF in the immune response fall into two main categories: A. Polarization of mature myeloid cells to a pro-inflammatory phenotype; B. Differentiation of progenitor cells into myeloid cells, expansion and mobilization to sites of inflammation.
(MF: macrophage Mo: monocyte Mc: monocyte-derived cell GC: granulocyte)
GM-CSF and Disease
GM-CSF is widely involved in various inflammatory diseases, especially cytokine storm-related inflammatory diseases (such as acute respiratory distress caused by new coronavirus or CAR-T) and autoimmune inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA). ) and giant cell arteritis (GCA), thus becoming an important target for the treatment of these diseases.
Current status of GM-CSF target drug development
At present, there is no drug approved for the GM-CSF target, and there are many drugs in the clinical or preclinical research stage, which are mainly divided into two categories: one is GM-CSF antibody drug, and the other is GM-CSFR antibody drug . These drugs have achieved good efficacy in a variety of indications, among which the TJM2 of Tianjing Bio, the mavrilimumab of Kiniksa, the Lenzilumab of Humanigen, and the otilimab of GSK have received high attention.
In response to the needs of GM-CSF target mechanism research, drug development and GM-CSF protein activity measurement, we have launched the hGM-CSF Effector Reporter Cell drug target cell model. Some of the data are shown below. Welcome to inquire.
hGM-CSF Effector Reporter Cell RQP74149
Figure 6. Dose Response of Recombinant Human GM-CSF in hGM-CSF Effector Reporter Cells (Clone 10).
Figure 7. Inhibition of hGM-CSF-induced Reporter Activity by hGM-CSF Neutralizing Antibody in hGM-CSF Effector Reporter Cells (Clone 10).

