How is the RET gene detected?
RET gene
Rearranged transfection (RET) is a class of genes found in every human cell. Abnormal activation of RET gene can lead to the occurrence and development of various tumors (thyroid cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, colorectal adenocarcinoma, etc.), which mainly include two variants: RET gene rearrangement/fusion and RET gene point mutation.
RET gene and disease
Patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC usually have age ≤60 years, non-smokers, less likely to have other oncogenic drivers, ≥10% signet ring cells in tumor cells, smaller size, earlier lymph node metastasis, low differentiation characteristics.
RET gene rearrangements/fusions occur in 10% to 20% of papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs), with a higher incidence in radiation-induced PTCs. To date, more than 35 partner genes have been rearranged/fused with the RET gene, with CCDC6-RET and NCOA4-RET being the most common forms in PTC. It has been reported in the literature that young thyroid patients with RET gene rearrangements/fusions tend to develop extracapsular invasion, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis at an early stage, and the stage is higher. RET gene point mutations include germline mutations and somatic mutations. Among them, germline mutation of RET gene is the basis for the formation and development of hereditary MTC (including MEN2A, MEN2B and familial MTC).
RET detection
There are four commonly used detection methods for RET gene rearrangement, namely real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), immunohistochemistry (IHC) and high-throughput sequencing (NGS).
The detection methods of RET gene point mutations mainly include qPCR, next-generation sequencing and NGS. qPCR is relatively sensitive and simple to operate, and is mainly used for the detection of known variant sites. Next-generation sequencing methods can discover new variant sites, but the sensitivity is lower than that of qPCR methods. NGS can detect multiple genes and multiple loci in parallel. Due to the wide detection range, new gene variants can be found.
We can provide diagnostic standards for various types of RET mutations to ensure the detection limit, sensitivity and stability of the diagnostic method.
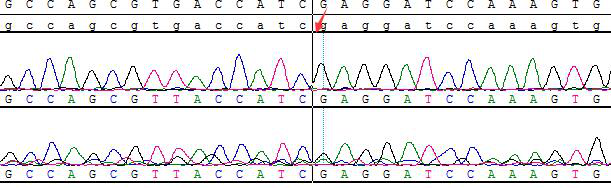
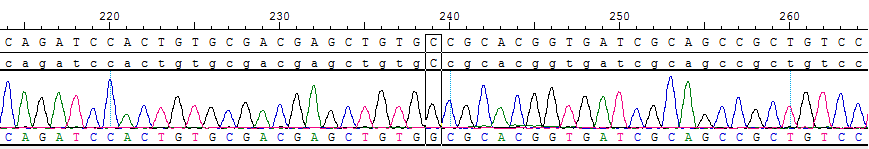
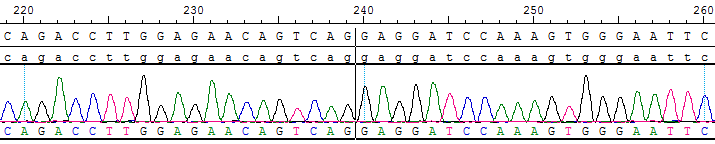
Part of the Sanger data map
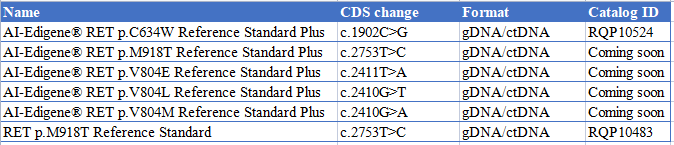
● AI-Edigene® RET p.C634W Reference Standard Plus RQP10524
● RET p.M918T Reference Standard RQP10483
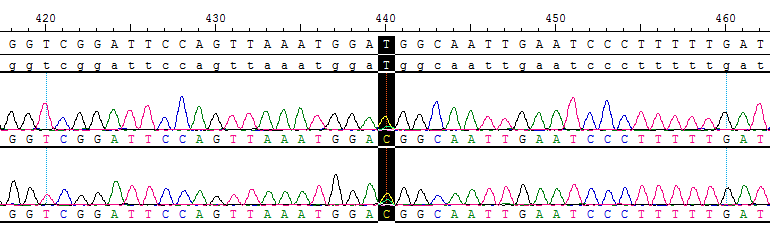
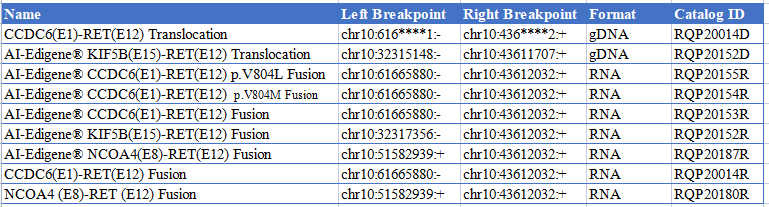
● AI-Edigene® KIF5B(E15)-RET(E12) Translocation RQP20152D
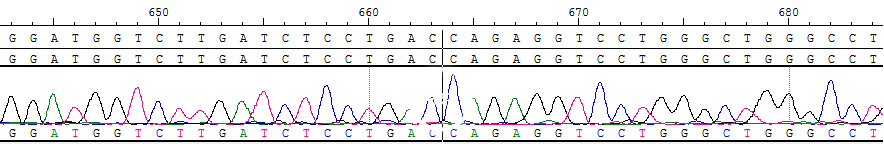
● AI-Edigene® CCDC6(E1)-RET(E12) p.V804L Fusion RQP20155R
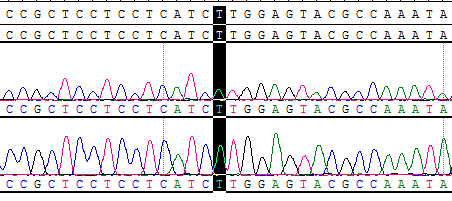
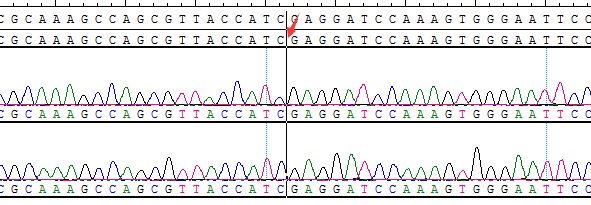
● AI-Edigene® CCDC6(E1)-RET(E12) p.V804M Fusion RQP20154R
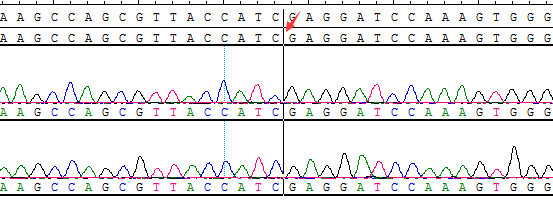
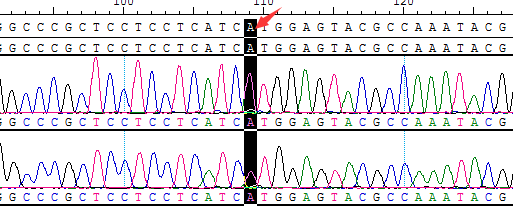
● AI-Edigene® CCDC6(E1)-RET(E12) Fusion RQP20153R
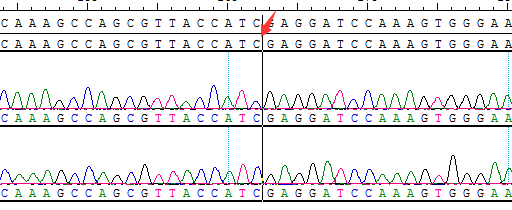
● AI-Edigene® KIF5B(E15)-RET(E12) Fusion RQP20152R
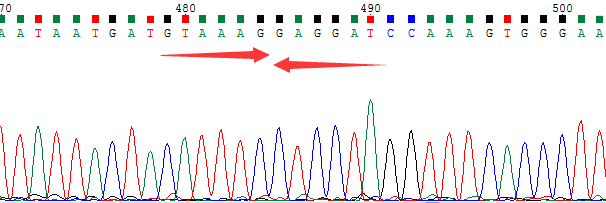
● AI-Edigene® NCOA4(E8)-RET(E12) Fusion RQP20187R
● CCDC6(E1)-RET(E12) Fusion RQP20014R