Popular CTLA4&PD1/L1 dual-target antibody activity detection cell model
T cells play a crucial role in different types of immune responses associated with cancer, infection and autoimmune diseases. The specific interaction of T cells with antigen-presenting cells often determines the fate of T cells and modulates their antitumor responses. Basic and clinical studies have found many immune regulatory molecules that regulate T cell function. Among them, immune checkpoint molecules expressed on T cells regulate T cell function by activating signals (co-stimulatory molecules) or inhibiting signals (co-inhibitory molecules). plays a central role in the immune system. At present, immune checkpoint antibody therapy targeting T cell function has achieved exciting efficacy and achieved great success, including targeting programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1. Monoclonal antibodies such as Pembrolizumab, Durvalumab and Ipilimumab against cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) have been widely used in patients with various tumors such as melanoma, metastatic urothelial carcinoma, bladder cancer, and lung cancer.
Among the immune checkpoint molecules discovered to date, the mechanism of action of CTLA-4 to suppress T cells is one of the most well understood. CTLA-4, also known as CD152, is a transmembrane glycoprotein that competes with CD28 for binding to CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2) proteins on antigen-presenting cells, and when bound to a ligand, Acting as an "off" switch for T-cell activation, CTLA4-targeting ipilimumab was the first immune checkpoint drug to be successfully used in melanoma patients.
PD-1 (also known as CD279), a T cell surface receptor, plays an important role in suppressing T cell activity through its interaction with its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2. Similar to CTLA-4 signaling, PD-1 binds its ligands to inhibit T cell proliferation, production of cytokines such as interferon-γ (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin 2 (IL-2), and to reduce Survival of T cells, but unlike CTLA-4, it mainly regulates effector T cell activity within tissues and tumors without affecting T cell activation in lymphoid organs.
Despite the remarkable success of immune checkpoint signaling through antibody drugs in cancer therapy, most patients currently do not benefit from single-target blockade. For example, although clinical antibody drugs targeting the PD-1 and CTLA-4 pathways have been used in a variety of cancer indications, the majority of patients are not effective with PD-1 or CTLA-4 blockade alone. Therefore, antibody combination therapy targeting more than one immune checkpoint antigen is considered a potentially effective strategy. Preclinical animal experiments have shown that combined blockade of CTLA-4 and PD-1 signaling can prolong animal survival in a B16 melanoma model and a K7M2 metastatic osteosarcoma model, while blocking CTLA-4 or PD-1 with antibodies alone The effect is limited. In clinical practice, antibody combination therapy of PD-1/L1 and CTLA4 has also been widely researched and applied. As early as 2015, the combination regimen of Nivolimab + Ipilimumab was the first to be approved by the US FDA for the treatment of melanoma, becoming the world's first marketed The dual IO combination program has been approved for multiple indications since then (kidney cancer, liver cancer and colorectal cancer, etc.).
In addition, AstraZeneca's I drug (Imfinzi) combined with tremelimumab has also achieved positive clinical results in different cancer types. In addition, some domestic pharmaceutical companies are also carrying out a number of similar clinical trials of combination drugs. For example, Harbin Pharmaceutical's CTLA4 antibody HBM4003 combined with Junshi Bio's PD-1 monoclonal antibody has been used in melanoma, advanced non-small cell Clinical trials have been carried out on lung cancer, advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, advanced neuroendocrine tumors/carcinomas and various other solid tumors; and Euho Pharma also announced a few days ago that NMPA has approved its innovative anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody YH003, anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody IND application for Phase I clinical trial of CTLA-4 mAb YH001 combined with anti-PD-1 pembrolizumab humanized mAb injection.
Although the combination therapy of CTLA-4 and PD-1/L1 has made good progress, in some clinical cases, the combination of the two did not achieve a multiplier effect, but increased the risk of toxic side effects, which may depend on different The clinical protocol and patient selection are also related to the double immunotoxicity caused by the simultaneous use of the two drugs. In addition, the combined use is often expensive, which is also a huge economic burden for tumor patients. In order to further improve the efficacy and reduce the toxic and side effects, with the development of double-antibody technology in recent years, double-antibody drugs targeting CTLA4 and PD-1/L1 are also under active development. The PD-1 x CTLA-4 dual-antibody drug in clinical trials entered Phase I clinical trials in Australia in October 2017. In China, in August last year, NMPA also granted priority review status for its new drug marketing application for the treatment of relapse Or metastatic cervical cancer, it is expected to become the first CTLA4/PD-1 bispecific antibody drug approved for marketing; and the PD-1 x CTLA-4 dual antibody drug MEDI5752 developed by foreign pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca is also closely followed. After that, it entered the clinic in Australia in April 2018; and KN046 developed by Corning Jereh is a dual-antibody drug targeting both CTLA-4 and PD-L1. At present, the drug is also available in Australia, China, and the United States. Approved for clinical trials, in different stages of clinical trials.
For the research and development of CTLA-4&PD-1/L1 antibody drugs, we have specially developed a CTLA&PD-1/L1 dual-target cell screening model, which can functionally measure and evaluate CTLA4&PD-1/L1 combination and dual characteristics from the cellular level The efficacy, product information and related data of the antibody are as follows:
PD-1/CTLA4 Dual Effector Reporter Cells RQP74150
PD-L1/CD80&CD86 aAPC Cells RQP74151
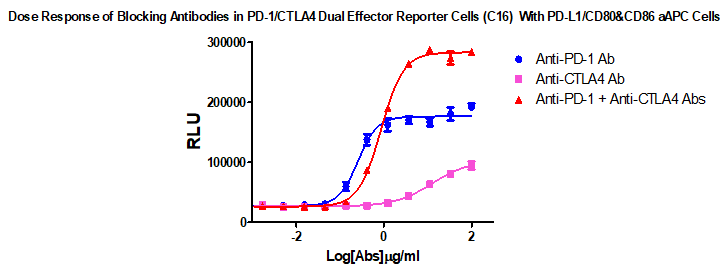
Fig 1. The CTLA-4+PD-1 Combination Reporter Assay reflects the mechanism of action of biologics designed to block the PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4/CD80&86 interaction. PD-1/CTLA-4 Dual Effector Cells were incubated with PD-L1/CD80&86 aAPC Cells in the presence of serial titrations of Anti-CTLA-4, Anti-PD-1 or both of the blocking Abs as indicated.
The reporter gene cell model can well reflect the molecular mechanism of action, and has less variability and better operability. Quality control and batch release are all important.
We attach great importance to R&D innovation. With the leading cell function transformation technology, high precision and flexible gene editing tool platform, we provide drug detection cell models including kinases, GPCRs, immunotherapy, drug resistance and other disease targets. At present, it has covered more than 400 spot cell models, and provides high-quality Cell-base biological assay services.
● T Cells Activation Assays (NFAT, IL2, NFkB….)
● Fc Effectors Activity Assays ( ADCC, ADCPs…)
● Immune Checkpoint Bioassays: Co-Inhibitory Targets (PD-1/PD-L1&2, TIGIT/CD155, CTLA4, LAG3, LILRB4/APOE, CD112R/CD112, SIRPa/CD47, TIM-3, BTLA/HVEM, CD161/CLEC2D, TIGIT&PD-1, LAG3&PD-1, CTLA4&PD-1 Combi…)
● Immune Checkpoint Bioassays: Co-Stimulatory Targets (OX40, 4-1BB, GITR, CD27, HVEM/LIGHT, CD28…)
● Cytokines and Growth Factor Assays ( BCMA, TGFβ, EGF, CSF1R,IL2, 15,IL4&13, IL6, IL11,IL12, IL23, IL36, IFNs,RANKL…)
● Others (TLR family members, STING,A2A family members, SARS Cov2…)

