Three years in review, Professor He knocked the wrong gene? CXCR4 or CCR5
In November 2018, gene-edited human babies Lulu and Nana were born "healthy". They are the world's first AIDS gene-edited babies. Professor He knocked out the CCR5 gene to block the binding of HIV to the CCR5 membrane protein on the surface of T cells. , Thereby blocking the invasion of viruses.
As soon as this incident occurred, there was a global uproar. Not only was it completely inconsistent and illegal in terms of ethics, laws and regulations, it was even questionable at the level of scientific research. The main manifestations were that the physiological functions of CCR5 were not very clear, and whether CCR5Δ32 had any disadvantages. The situation is more than profitable; the second is that the off-target effect caused by Crisper's gene knockout is uncontrollable; the third is that among the HIV strains, a large proportion of the current epidemic in China is CXCR4 tropism, not CCR5. Today we will talk about the CXCR4 and CCR5 genes.
Both CXCR4 and CCR5 belong to the family of chemokine receptors, which are a class of 7-pass transmembrane proteins and belong to the GPCR category. The chemokine receptor family can be divided into four subfamilies: CC, CXC, CX3C, and C chemokines according to the positions of the two conserved cysteine residues at the N-terminus. Among them, CXCR4 belongs to the CXC family, and CCR5 belongs to the CC family.
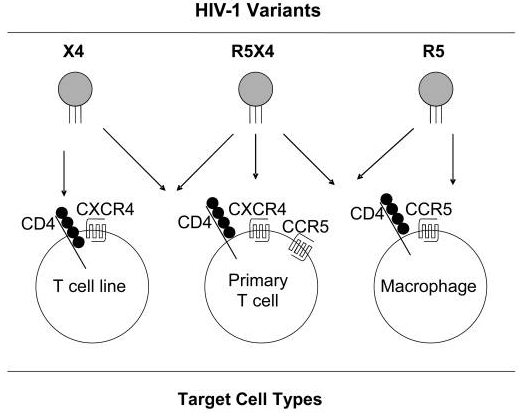
Fig 1. The ability of different subtypes of HIV virus to infect T cells
CXCR4 gene and its function
SDF-1α activation of CXCR4 can trigger a variety of physiological responses, such as chemotaxis, cell survival and proliferation, intracellular calcium flux and gene transcription, while CXCR4 antagonists cannot. These normal physiological responses also share several downstream effectors with multiple pathological processes, including tumor cell metastasis, HIV-related dementia (induced by HIV-1 gp120), and autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
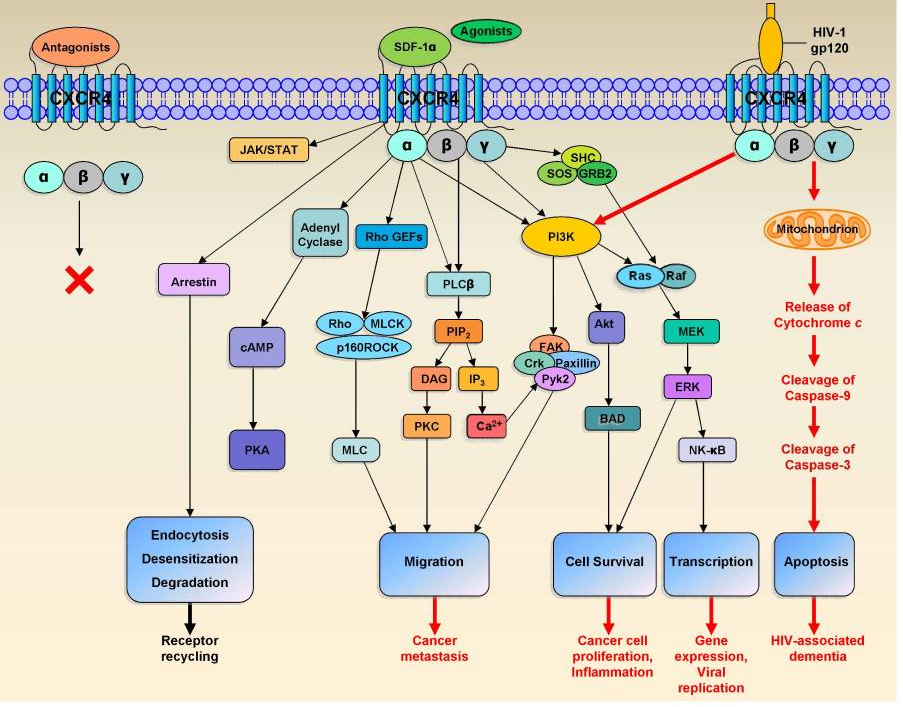
Fig 2. Signal conduction and function of CXCR4
The main functions of CXCR4 can be divided into:
● Firstly, CXCR4 antagonists can fight HIV infection;
● CXCR4 antagonists and agonists play an important role in the treatment of hematopoietic and solid cancer;
● CXCR4 antagonists fight inflammation and autoimmune diseases: rheumatoid arthritis and allergic asthma.
CCR5 gene and its function
Since its discovery, CCR5 has been a key participant in HIV-1's entry into target cells, and together with its chemokine ligands, has helped to understand and resolve HIV-1 infection. CCR5 dominates the chemokine co-receptor used by HIV-1 for cell entry, and the R5-tropic HIV-1 strain is the most frequently transmitted strain in the early stages of infection. The 32-base pair deletion in the CCR5 gene results in non-functional gene products that cannot reach the cell surface, and subjects with homozygous CCR5Δ32 deletion can be protected from HIV-1 infection, which is also the target base modified by Professor He.
CCR5 may also be related to the development of various cancers, because tumor cells directly secrete or induce fibroblasts to secrete CCL5, thereby maintaining the proliferation of CCR5-positive cancer cells. In addition, CCR5 may play a role in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis (MS).
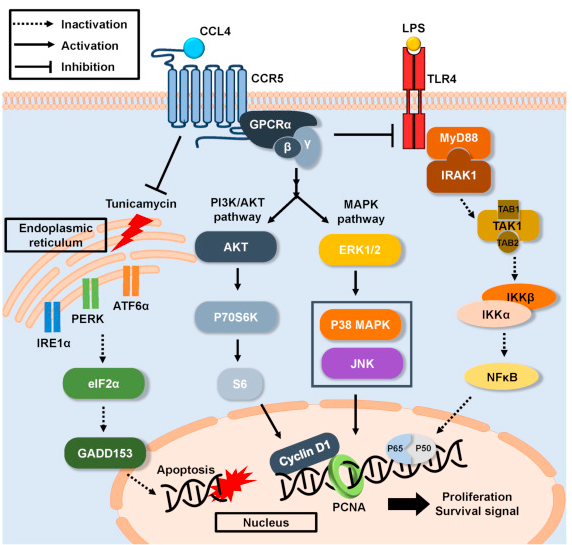
Fig 3. Signal conduction and function of CCR5
Target Model Products-Test Activity and Release
We have developed a series of cell models for GPCR targets, including CXCR4, CCR5 and other members of the chemokine family, such as CXCR2, CCR1, CCR2, CCR4, CCR6, CCR7, etc. This cell model is suitable for the detection of the activity of targeted drugs, and is suitable for QC release of drugs.
Related Products
CXCR4/CHO RQP71358
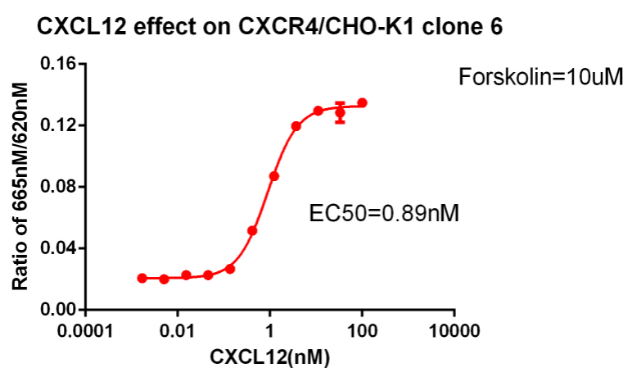
Fig 4. CXCR4 is the GPCR target of the Gi pathway and can detect changes in cAMP. Use 10uM forskolin to stimulate cAMP to detect the activity of agonist (CXCL12).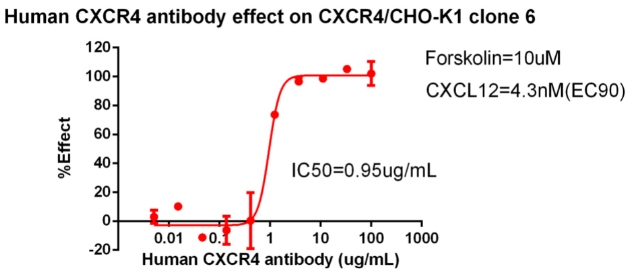
Fig 5. For the antagonist model of CXCR4, 10uM forskolin was used to stimulate cAMP, and the EC90 effect of CXCL12 was used to detect the antagonistic effect of CXCR4 antibody.
CCR5/CHO RQP71352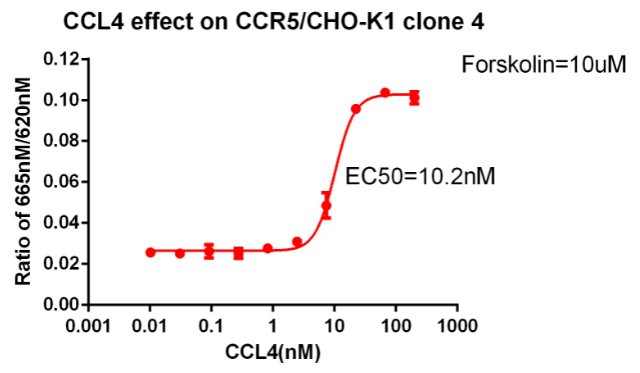
Fig 6. CCR5 is the GPCR target of the Gi pathway and can detect changes in cAMP. Use 10uM forskolin to stimulate cAMP to detect the activity of agonist (CCL4).

