[Target model + diagnostic quality control] Drug development and diagnosis of BTK C481S
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK for short) is a tyrosine kinase encoded by the BTK gene. BTK contains 5 different protein interaction domains, including the amino-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, the proline-rich TEC homology (TH) domain, and the SRC homology (SH) domains SH2 and SH3. And the domain with kinase activity.
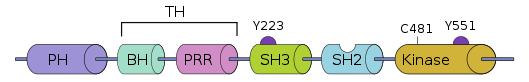
Fig 1. The domain of BTK
BTK plays a vital role in the development of B cells, because it is necessary to transmit signals from the pre-B cell receptors formed after the successful rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy chains. It also plays a role in hypertrophy through high-affinity IgE receptors. Play a role in cell activation. BCR activation triggers the formation of signal bodies, which include protein tyrosine kinases LYN, SYK, and BTK, as well as phospholipase Cγ2 and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. In the signaling body, BTK is phosphorylated by LYN and SYK. SYK and BTK then phosphorylate phospholipase Cγ2, leading to calcium mobilization, activating ERK, AKT, and nuclear factor-κB, which subsequently leads to cell survival, cell proliferation, differentiation, and antibody production.
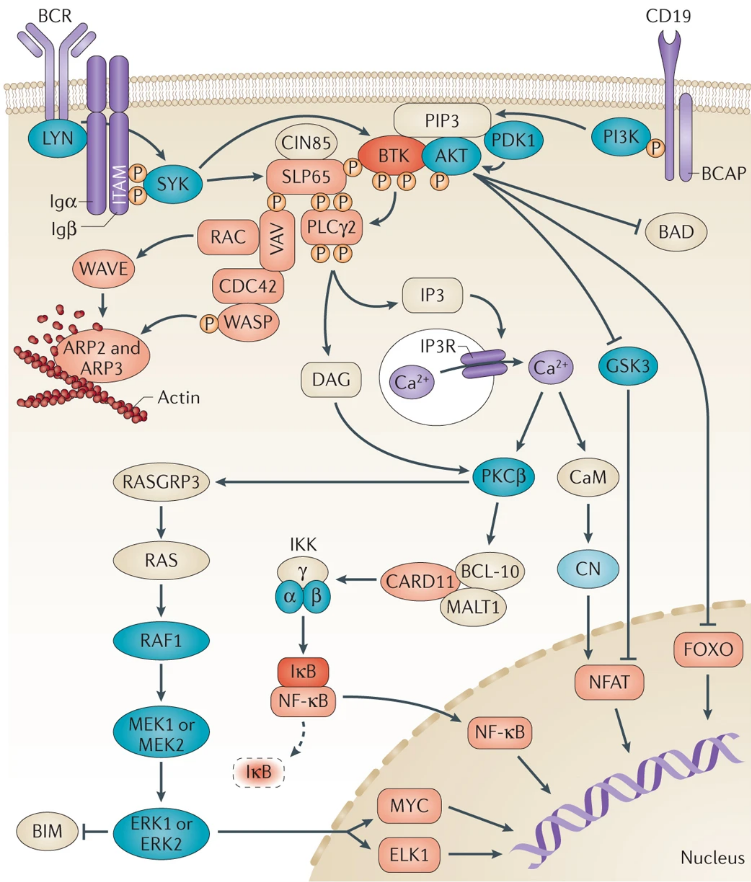
Fig 2. Signal pathway involved in BTK
Inhibitors of BTK
BTK is expressed in many B-cell leukemias and lymphomas. As early as 1999, the first rationally designed small molecule inhibitor of BTK (LFM-A13) was shown to have anti-leukemia activity in vitro, and more selective subsequently A number of BTK inhibitors, including the irreversible inhibitor Ibrutinib (also known as PCI-32765) have been developed one after another. Ibrutinib is used to demonstrate that BTK is involved in oncogenic BCR signaling, which controls the survival of the human activated B-cell-like subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (ABC-DLBCL). Ibrutinib monotherapy has shown encouraging clinical activity in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in phase II trials. Therefore, Ibrutinib received a breakthrough designation and was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2013 for the treatment of recurrent MCL.
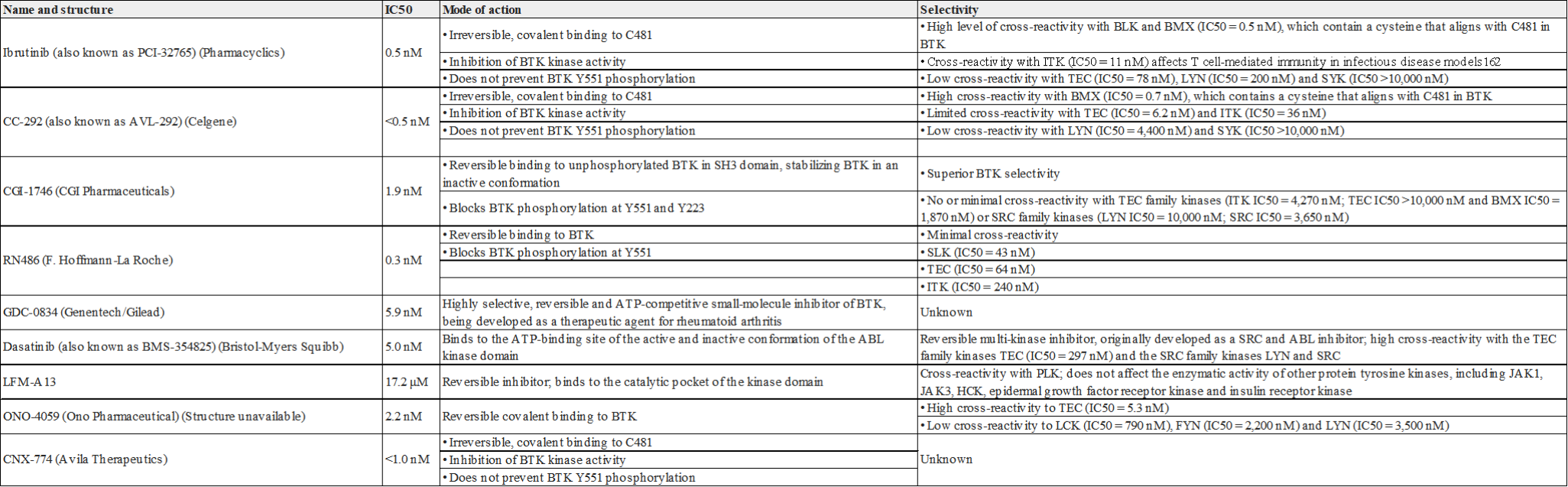
Fig 3. Common BTK small molecule inhibitors targeting B cell tumors
Ibrutinib is an oral inhibitor that can covalently bind to cysteine 481 of BTK. It has been clinically found that BTK C481S mutations appear in CLL patients who have progressed after ibrutinib treatment, destroying Ibrutin The covalent binding of Nitrogen and BTK reduces the inhibition of BTK enzyme activity. Therefore, the second-generation non-covalent BTK inhibitor does not need to be combined with C481. At the same time, the recent hot BTK inhibitors belong to BTK- PROTAC.
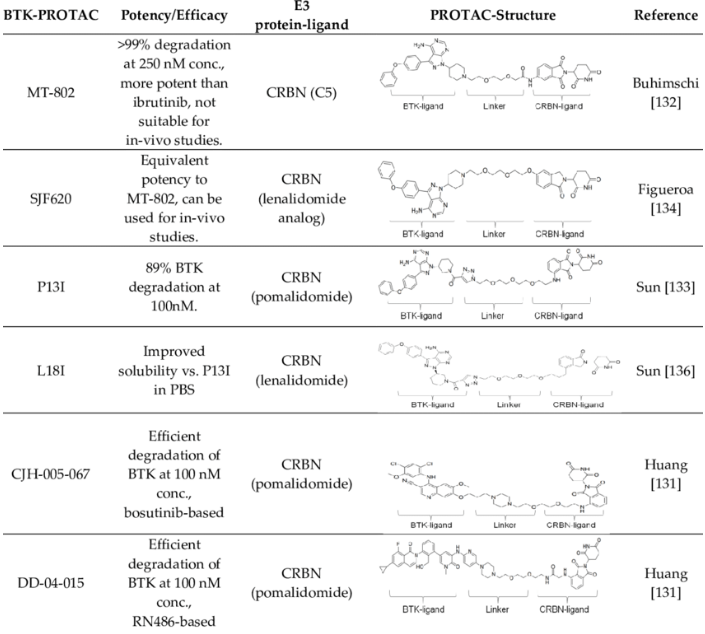
Fig 4. Common PROTAC molecules targeting BTK
Diagnosis of BTK C481S
The detection of BTK C481S directly affects the treatment plan of ibrutinib. Therefore, no matter what method is used in the clinic, it is necessary to detect this site.
Standard
As a company specializing in providing molecular diagnostic standard products, Kebai Biotech provides various forms of products for BTK C481S (gDNA, ctDNA, FFPE, etc.), involving multiple technology platforms, and quality control management for the entire process, which is also suitable for LDT And IVD development verification.

Table 1. Molecular diagnostic standards of BTK C481S
Part of the data display
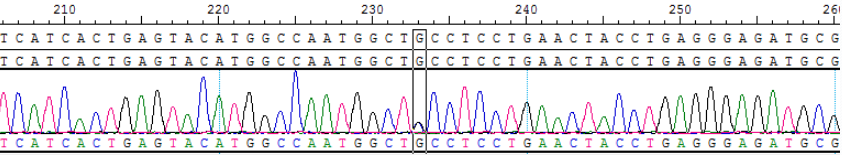
Fig 5. Sanger sequencing of BTK C481S for DNA
Drug target model
For the drug target model of BTK C481S, at the cell-based assay level, we constructed a model based on BTK C481S-driven baf3, which can be used to screen small and macromolecules resistant to C481S; at the same time, we also constructed BTK overexpressing models. Stable cell lines can be used in PROTAC technology.
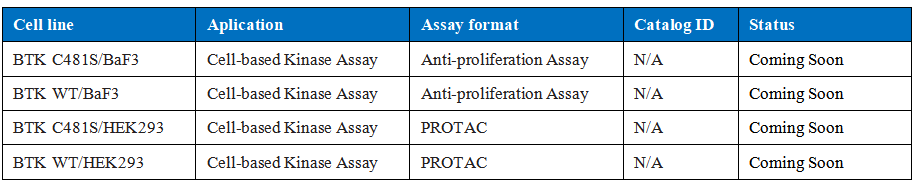
Table 2. Cell-based assay of BTK include anti-proliferation and PROTAC
部分数据展示
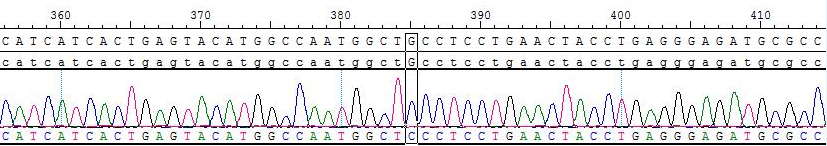
Fig 6. Sanger sequencing of BTK C481S for RNA

