TIGIT&PD-1/L1 dual target cell screening model
The human immune system is regulated by a complex network composed of various inhibitory and stimulatory receptors. These two types of receptors promote the immune response to eliminate pathogens while maintaining tolerance to self-antigens. Inhibitory immune checkpoint receptors have been shown to play an important role in the development of cancer and autoimmune diseases in addition to playing a key role in maintaining immune balance. Many proteins expressed on various immune cells, including PD-1, CTLA4, TIGIT, LAG3, etc., have been identified as inhibitory immune checkpoint receptors. Monoclonal antibodies are used to block the interaction between these receptors and their ligands. Combination has been proven to be an effective strategy to enhance the anti-tumor immune response and promote immune-mediated tumor rejection.
The most representative inhibitory immune checkpoint receptor is the programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1), also known as CD279. Its expression mainly occurs after the activation of T and B lymphocytes. The binding of ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 can directly inhibit T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated signal transduction, thereby inhibiting the activation and proliferation of T cells and the production of cytokines. According to the mechanism of PD-1's involvement in immunosuppression, many blocking antibodies against PD-1 or its ligand PD-L1 have been developed as immune checkpoint inhibitor drugs, and have been marketed. At present, they have been widely used in various clinical applications. In the immunotherapy of tumor, great success has been obtained.
Although PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors have achieved great success in the field of tumor immunity, their overall effective rate in most types of tumors is not more than 50%, and the average effective rate of single drugs for most types of tumors is The efficiency is only about 20%, and a large number of patients have been found to have primary and acquired drug resistance in the process of clinical application. This has prompted people to consider other immune checkpoint receptors as targets and develop new drugs and therapies. Replacement and supplement of existing PD-1/PD-L1 drugs.
Among them, TIGIT, as a new immune checkpoint, has only a short period of more than ten years from function confirmation to widespread attention. It is an immune checkpoint receptor expressed on lymphocytes, and high levels of expression can usually be observed on effector CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, regulatory T cells and NK cells. TIGIT has several different mechanisms of inhibiting lymphocyte activation: First, it is an inhibitory receptor that has the opposite effect of the costimulatory receptor CD226. When TIGIT exists on the surface of lymphocytes, it acts against CD226. The affinity of the common ligand CD155 is higher than that of CD226. Therefore, TIGIT will preferentially bind to CD155, thereby blocking the costimulatory effect of CD226. Secondly, TIGIT can block CD226 by inhibiting the formation of CD226 homodimer. Signal; In addition, the cytoplasmic tail of TIGIT contains a tyrosine-based immunoreceptor inhibitory motif (ITIM), which may cause signal suppression. Some evidence suggests that this is the main mechanism by which TIGIT induces T cell suppression.
As the first TIGIT inhibitor to enter clinical trials, Roche’s TIGIT monoclonal antibody Tiragolumab showed very impressive clinical data at ASCO in 2020, which is impressive. Compared with Atezolizutmab alone, Tiragolumab combined with Atezolizutmab can significantly improve PD-L1. The overall response rate of patients with expressing non-small cell lung cancer, the objective response rate (ORR) has nearly doubled (31.3% vs 16.2%), and the median progression-free survival (PFS) has also been extended from 3.6 months to 5.4 months. The risk of disease progression is reduced by 43%, which shows significant clinical significance.
In addition to Roche, many leading well-known pharmaceutical companies at home and abroad have also deployed this target in their pipeline.
Although the development of TIGIT monoclonal antibody drugs is in full swing, this type of drug has a big drawback, that is, its single-drug efficacy is very poor. Compared with PD-1 drugs, there is almost no chance of winning. It can only be considered to target TIGIT and PD at the same time. -1/L1 to PK PD-1/L1 single drug efficacy. Therefore, the TIGIT project that has already carried out clinical trials has all adopted the combination with PD-1/L1 monoclonal antibody.
In addition to improving the efficacy of combined drugs, with the development of bispecific antibody technology, the development of bispecific antibody drugs targeting TIGIT and PD-1/L1 at the same time is also a promising R&D strategy. Recently, Cinda has taken the lead in announcing that the Phase 1a clinical trial of the anti-PD-1/TIGIT bispecific antibody IBI321 jointly developed by it and Eli Lilly has completed the first patient administration. There are other companies with similar targets. Bispecific antibodies are in the pre-clinical development stage.
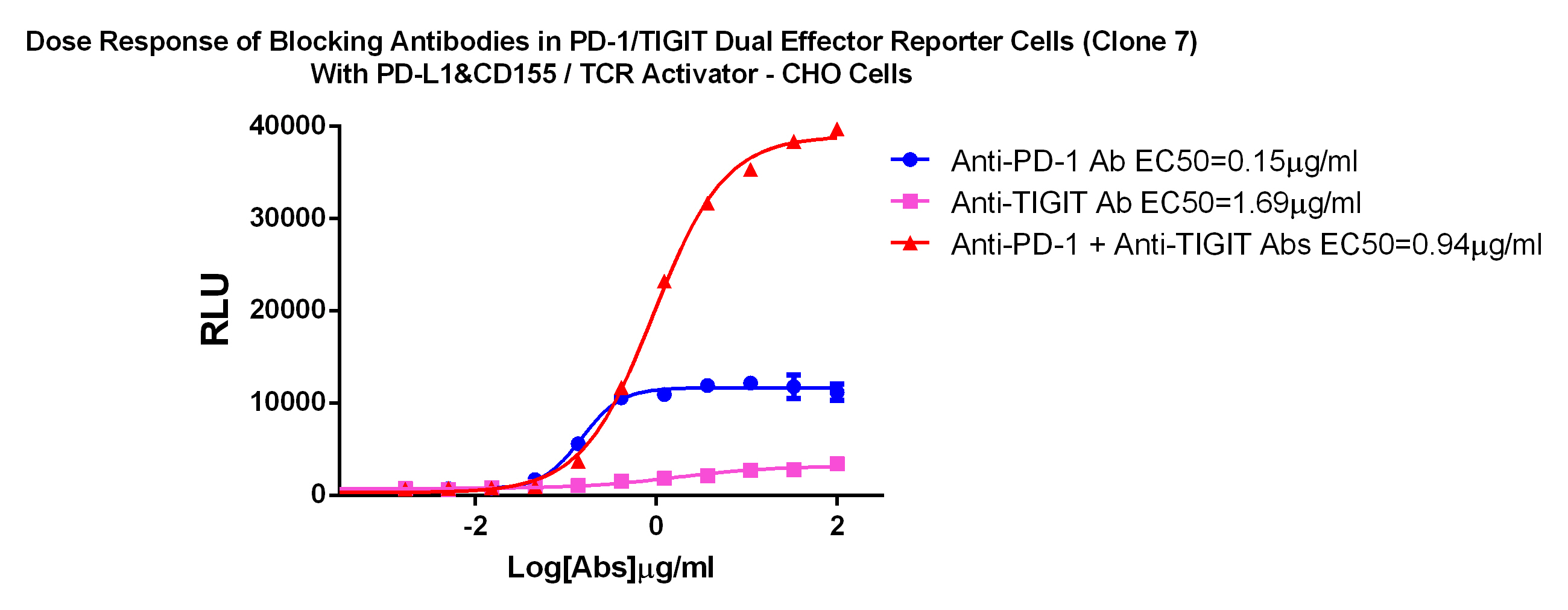
For the research and development of TIGIT&PD-1/L1 antibody drugs, we have specially developed TIGIT&PD-1/L1 dual target cell screening model, which can measure the activity and evaluate the TIGIT&PD-1/L1 combination drug and dual-specific antibody at the cellular level. Medicinal effect.
PD1/TIGIT Dual Effector Reporter Cell RQP74126
PDL1/CD155/TCR Activator/CHO RQP74127