[Target model + diagnostic quality control] Drug development and diagnosis of common mutations in c-Kit
c-Kit is a type III receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), which plays a vital role in the development of cancer. At present, c-Kit is mainly considered as a stem cell factor (SCF), which is involved in important functions of the human body, such as fertility, homeostasis and melanin production; nevertheless, early studies on c-Kit introduced it as an oncogene. Disorders of c-Kit, including overexpression and gain-of-function mutations, have been detected in several human diseases. Such as piebaldism, gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), systemic mastocytosis, acute myeloid leukemia and so on.
c-Kit is a proto-oncogene in the long arm region of chromosome 4 (4q11-4q13), which encodes the SCF receptor (CD117). It consists of five IgG-like extracellular domains, a transmembrane helix, and an autoinhibitory The near membrane (JM) domain is composed of a cytoplasmic kinase domain.
c-Kit signal pathway
c-kit involves a variety of signaling pathways, including Ras-Erk Pathway, PI3K/AKT pathway and Src-signaling pathway. Although each signal pathway has different effects on cell function through different pathways, the result of the three pathways is to inhibit cell apoptosis and lead to tumorigenesis in different ways, such as inducing cell proliferation and growth.
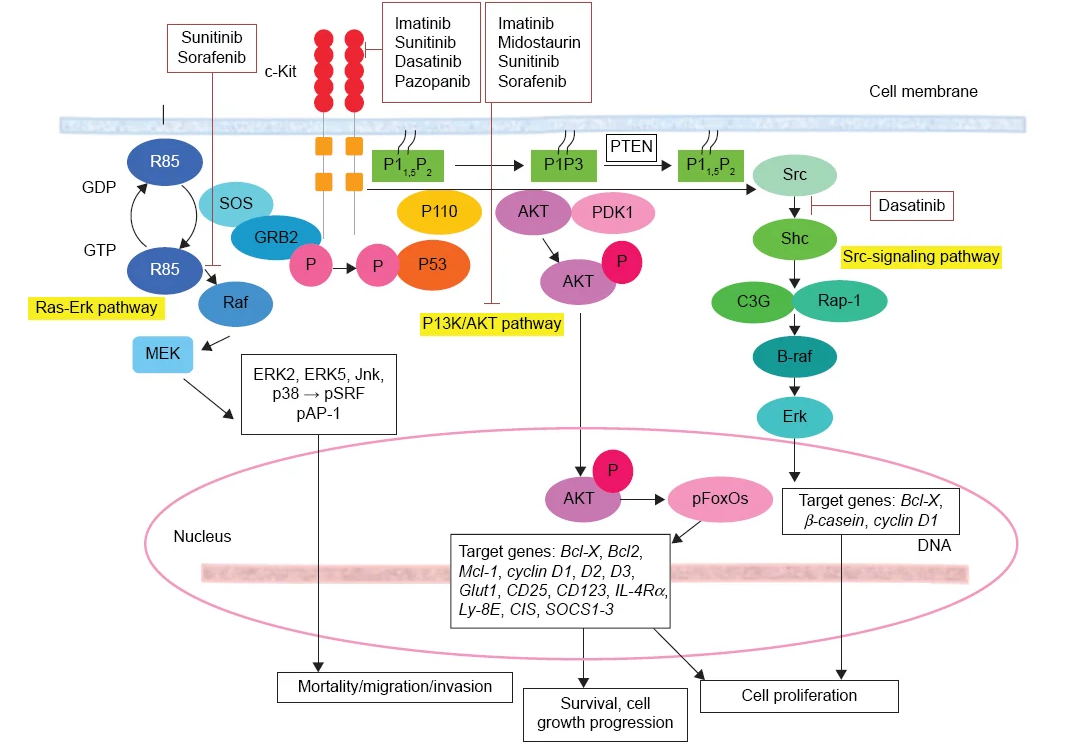
Figure 1. Signal pathways related to c-Kit
Common mutations in c-Kit
Many Kit mutation sites have been discovered so far, and they are different in different cancer types, reflecting the impact of each mutation on downstream signaling pathways. Some "hot spots" in Kit genes are regular in some major domain structures. For example, intracellular and extracellular juxtamembranes are located in exon 8, 9 and exon 17, which correspond to the activation loop in the kinase domain. These mutations destroy the self-inhibitory effect of c-Kit.
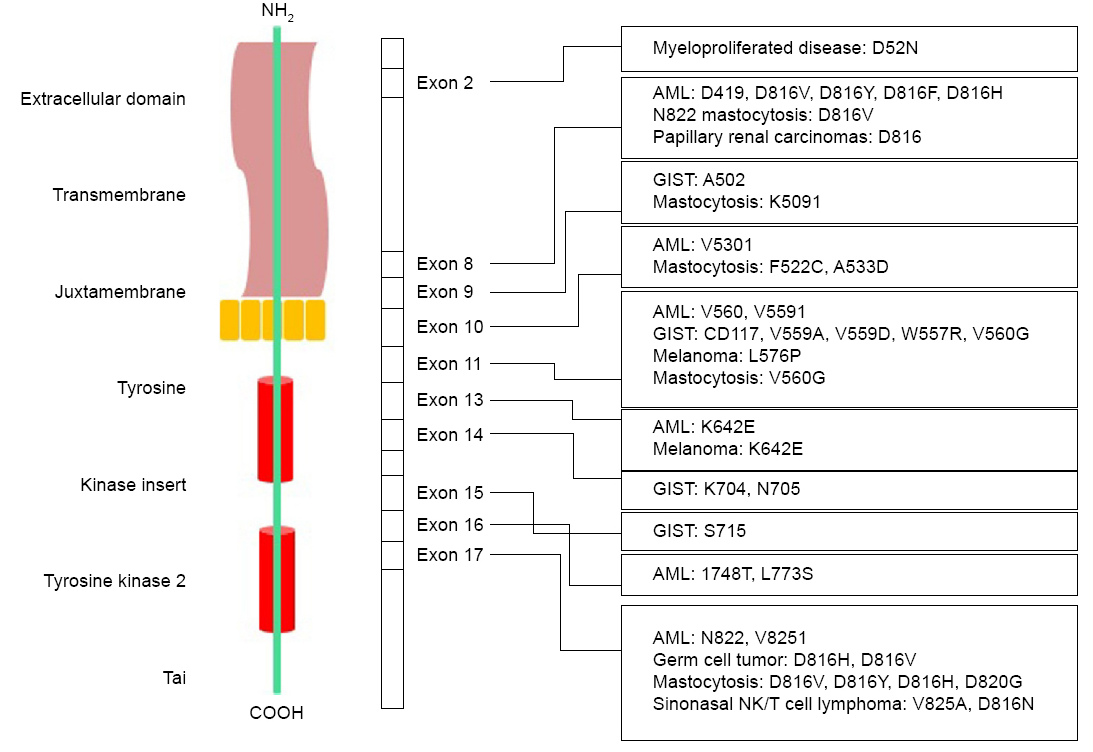
Figure 2. Common c-Kit mutations
Diagnosis of c-Kit
According to the NCCN guidelines, about 80% of GISTs have mutations in the tyrosine kinase receptor encoding gene KIT. When they have exon 11 mutations, nearly 90% of patients can benefit from imatinib treatment; When sub-9 is mutated, nearly 50% of patients can benefit from imatinib treatment.
In the AML guidelines, it is described that approximately 20% of CBF (core binding factor) AML patients have KIT mutations. Recommended molecular tests include c-KIT, FLT3 [ITD and TKD], NPM1, CEBPA (biallelic), IDH1, IDH2 , TP53, and other mutations.
Standard
As a company specializing in providing molecular diagnostic standards, we provide a variety of common mutation forms of c-kit products (gDNA, RNA, ctDNA, FFPE, etc.), involving multiple technology platforms, and quality control management for the entire process. It is also suitable for the development and verification of LDT and IVD.
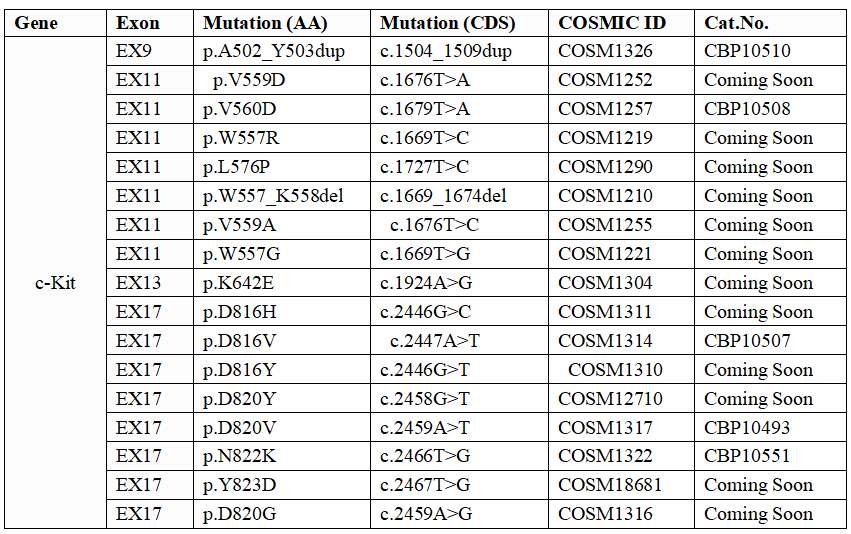
Table 1. Molecular diagnostic standards for common c-kit mutations
Part of the data display 
Figure 3. c-KIT p. A502_Y503dupwith sanger sequencing
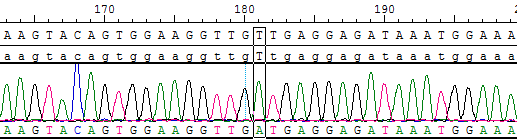
Figure 4. c-Kit p.V560D with sanger sequencing
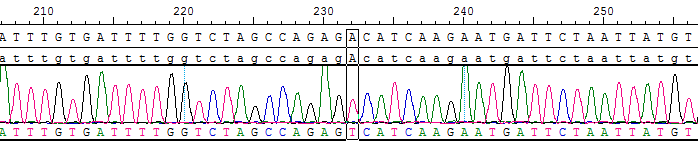
Figure 5. c-Kit p.D816Vwith sanger sequencing
c-Kit mutant drug development
In the natural state, the catalytic activity of c-Kit remains auto-inhibited until the ligand SCF binds to initiate the homodimer of c-Kit, the monomers of c-Kit rearrange, and the JM domain is released from auto-inhibition. A The ring switches from the inactive position to the active position. Our common c-kit mutations often directly lead to the dimerization and activation of c-Kit without the need for ligand SCF binding.
Imatinib is approved as a first-line treatment for patients with resectable primary GIST and those with unresectable or advanced metastatic GIST. These mutations are generally caused by Exon11. However, the first-line treatment induced acquired secondary mutations mainly appear in Exon13/14 and 17, these mutations will directly activate the A ring, and thus are not sensitive to many inhibitors including imatinib.
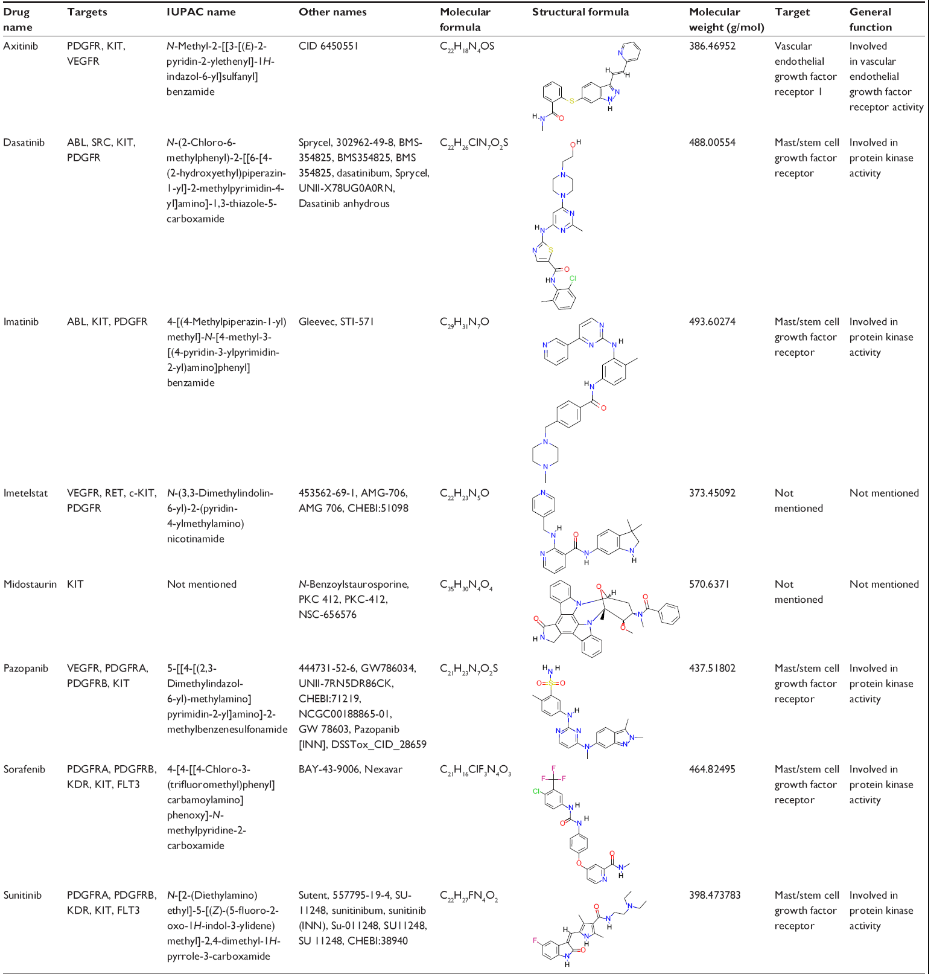
Figure 6. Common c-Kit inhibitors
Drug target model
For c-Kit and its common drug resistance sites, we have developed a variety of cell-based kinase assay models, which can be used for in vitro and in vivo activity detection of TKI, which is suitable for early detection of compound activity, and also suitable for late stage The products are released by QC.
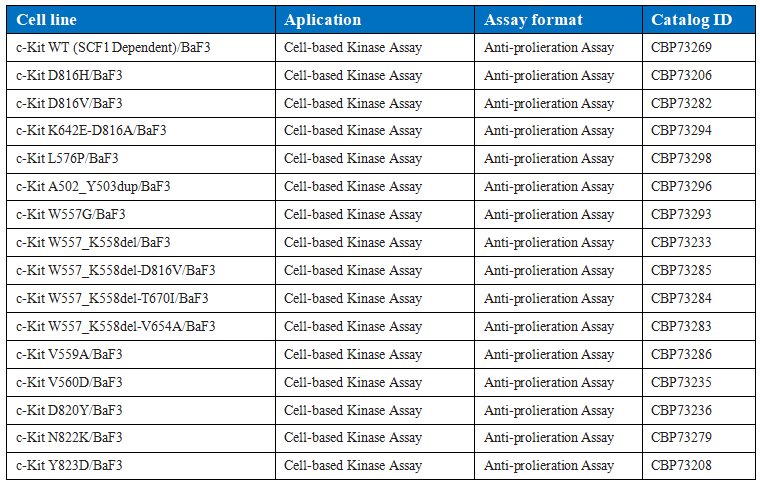
Table 2. Drug target models of some common c-kit mutations
Part of the data display
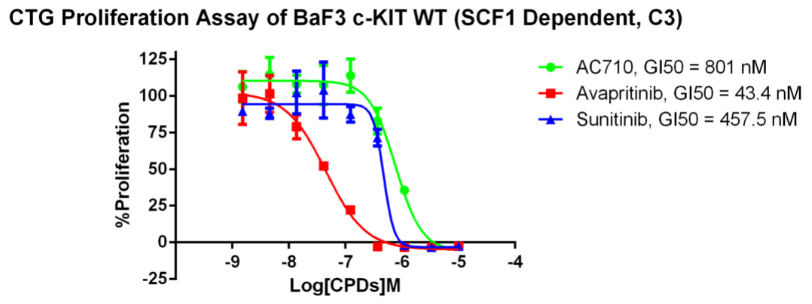
Figure 7. Anti-proliferation assay of three reference compounds on the c-Kit WT (SCF1 Dependent)/BaF3 Stable Cell Line.
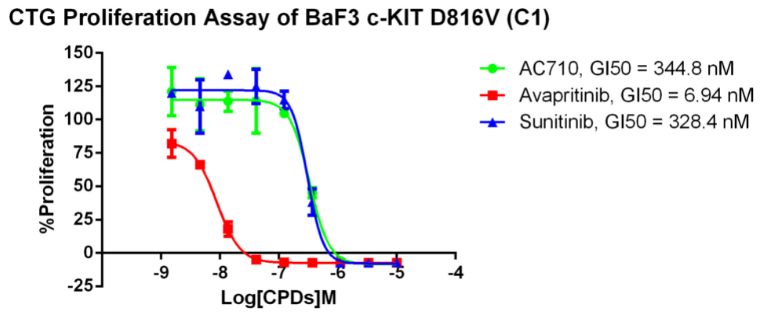
Figure 8. Anti-proliferation assay of three reference compounds on the c-Kit D816V/BaF3 Stable Cell Line.
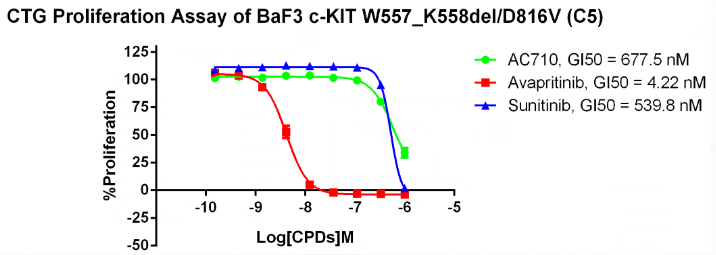
Figure 9. Anti-proliferation assay of three reference compounds on the c-Kit W557_K558del-D816V/BaF3 Stable Cell Line.

