【Product Promotion】GLP1 Drug Target Model
In healthy humans, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is secreted after eating and reduces glucose concentration by increasing insulin secretion and inhibiting the release of glucagon. Other effects of GLP-1 include delayed gastric emptying, suppression of appetite, stimulation of β cell proliferation and differentiation, and inhibition of β cell apoptosis.
The native GLP-1 is degraded within 2-3 minutes in the circulation. Therefore, various GLP-1 receptor agonists have been developed to provide long-term effects in vivo. These GLP-1 receptor agonists can be classified as short-acting compounds, which provide short-term receptor activation (such as exenatide and lixisenatide) and long-acting compounds (such as albiglutide, dulatide) Lutide dulaglutide, long-acting release exenatide and liraglutide) continue to activate GLP-1 receptors at the recommended dose. The pharmacokinetic differences between these drugs have led to important differences in their pharmacokinetic profiles. Short-acting GLP-1 receptor agonists mainly reduce postprandial blood glucose levels by inhibiting gastric emptying, while long-acting compounds have a stronger effect on fasting blood glucose levels, which are mainly mediated by the resting effect of insulin and glucagon . The distribution of adverse reactions of these compounds is also different.
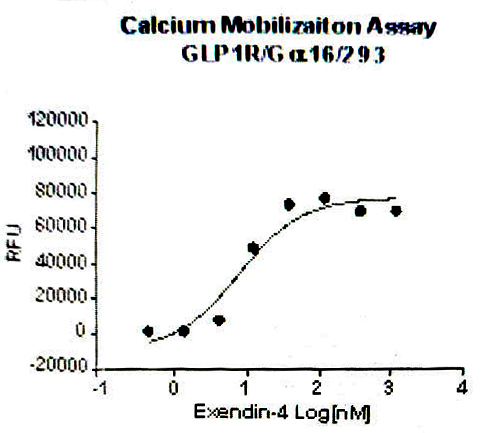
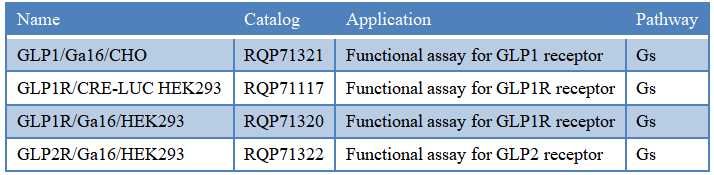
GLP-1 receptor agonist drugs are still an important direction for the development of hypoglycemic drugs. In order to facilitate the research and development of pharmaceutical companies, we can provide the following drug target cell models for the detection of the activity of such compounds.
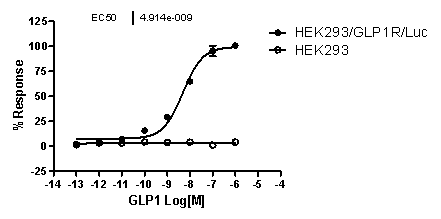
GLP1R/CRE/Luc HEK293 RQP71117
GLP1R/Ga16/HEK293 RQP71320