FGFR3-TACC3 Fusion Drug Cell Screening Model
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and aggressive primary brain cancer in adults. In 2009, it was first reported that the FGFR3-TACC3 fusion gene exists in GBM. In recent years, studies have found that about 3% of GBM patients have the FGFR3-TACC3 fusion gene, and it also has a certain proportion in other tumors such as bladder cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. The fusion gene can be detected, and GBM and bladder cancer overexpressed by the fusion gene are highly aggressive. Therefore, FGFR3-TACC3 fusion may become a new GBM subtype and a potential therapeutic target.
In 2017, after the analysis of the second-generation sequencing gene detection of more than 10,000 advanced cancer patients, it was found that 29 cases of FGFR3 fusion, of which 13 cases of glioma accounted for 2.54% (13/512), and the fusion partner TACC3 accounted for 12 cases, accounting for 92.31%. (12/13), ST7L is 1 case accounting for 7.69% (1/13); Bladder cancer is 6 cases accounting for 1.48% (6/405), Fusion partner TACC3 is 4 cases accounting for 66.67% (4/6), JAKMIP1 is 1 Cases accounted for 16.67% (1/6), TNIP2 accounted for 1 case accounted for 16.67% (1/6); 5 cases of non-small cell lung cancer accounted for 0.32% (5/1563), fusion partner TACC3- accounted for 4 cases accounted for 80.00% (4 /5), 1 case of CXorf26 accounted for 20.00% (1/5); 1 case of germ cell tumor accounted for 0.36% (1/236), fusion partner was TACC3; 1 case of endometrial cancer accounted for 0.48% (1/210) , The fusion partner is TACC3; 1 case of head and neck cancer accounts for 0.60% (1/166), and the fusion partner is TACC3.
Existing research shows that FGFR3-TACC3 fusion protein has the following two effects on tumors:
(1) The FGFR3-TACC3 fusion protein can activate the PIN4 protein, increase the number of peroxisomes in the cell, release a large amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS), induce the production of PGC1α, enhance mitochondrial metabolism, promote protein synthesis, and stimulate tumor growth .
(2) Activate PI3K-AKT, RAS-MAPK, JAK-STAT3 signal pathways, promote cell proliferation, and lead to tumorigenesis or drug resistance.
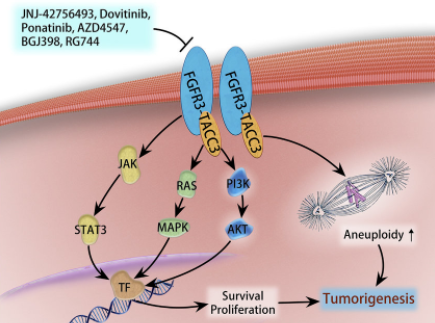
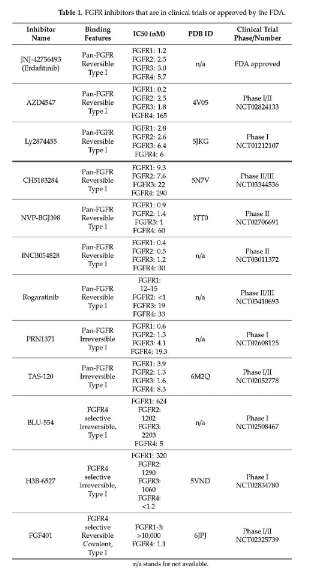
Research on the FGFR3-TACC3 fusion target in GBM and other tumors such as bladder cancer and non-small cell lung cancer is currently in the clinical development and marketing stage. Currently on the market is Janssen Pharmaceuticals Balversa (Erdafitinib), an oral pan-FGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor. It was approved by the FDA in 2019. The indication is locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer carrying FGFR3/2 gene mutation or fusion. (MUC) adult patients. Other drugs currently in the clinical stage are mainly pan-FGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, such as Ponatinib, Infigratinib, AZD4547, BGJ398, RG744, etc. Among them, BGJ398 is progressing rapidly at present, which is in the second clinical stage, mainly for adult GBM patients with FGFR1-TACC1, FGFR3-TACC3 fusion or FGFR1/2/3 activating mutations.
In response to the development and research needs of FGFR3-TACC3 fusion inhibitors, we have developed the FGFR3-TACC3/BAF3 drug sieve cell line. Welcome to inquire.
FGFR3 TACC3/BaF3 RQP73297
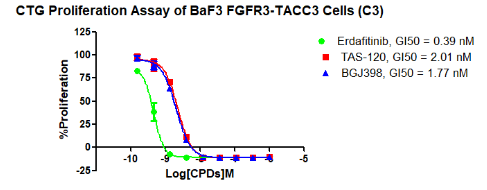
Figure 2. CTG Proliferation Assay of BaF3 FGFR3-TACC3 Cells (C3).

