[Product Promotion] CD47&SIRPɑ Cell Screening Model
CD47 is also known as antigen surface determinant protein OA3, integrin-related protein (IAP) and protein MER6. It is a five-pass transmembrane protein and belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. Its N-terminal extracellular region contains an Ig-like type V (immune Globulin-like) domain. CD47 is widely distributed in various tissues, and affects cell apoptosis, proliferation, and immunity by interacting with signal regulatory protein ɑ (Signal regulatory ɑ, SIRPɑ), thrombospondin-1 (TSP1) and integrins (Integrins). And a series of physiological functions.
SIRPɑ belongs to the SIRP family and is an inhibitory immune receptor. It is usually selectively expressed on the membrane surface of myeloid cells (macrophages, granulocytes, dendritic cells, etc.) and nerve cells, and on other somatic cells. There is less expression. As a transmembrane protein, there are three immunoglobulin domains in its extracellular domain, and the N-terminal amino acid terminal structure can bind to CD47 to mediate cell signal transduction.
The CD47/SIRPɑ signaling pathway plays an important role in regulating the phagocytic function of macrophages. CD47 binds to SIRPɑ on the surface of macrophages to phosphorylate its ITIM, and then recruit its downstream protein SHP-1 to produce a series of cascade reactions. Inhibit the phagocytosis of cells. Young red blood cells usually express higher levels of CD47, so they release a "don't eat me" signal to macrophages, while aging red blood cells are eventually phagocytosed and cleared by macrophages due to the down-regulation of CD47 expression.
Since CD47 is highly expressed in almost all tumor cells and tissues, tumor cells will use the interaction mechanism between CD47 and SIRPɑ on the surface of macrophages to escape the phagocytosis of macrophages.
As we all know, tumor immunotherapy is currently the hottest research and development direction of tumor drugs. Among them, antibody drugs represented by the inhibition of PD-1/PD-L1 interactions have achieved great success and have triggered an influx of many players, which has made competition increasingly fierce, which has also prompted people to continue to find and explore new research and development hotspots. . In a sense, CD47/SIRPɑ has a certain target similarity with PD1/PD-L1. Tumor cells can bind to PD-1 on the surface of T cells by expressing PD-L1, and release something like "Don’t find me ( Do not find me)” signal to escape the surveillance and attack of T cells; and the combination of CD47 and SIRPa releases the “Do not eat me” signal, which allows tumor cells to escape the phagocytic attack of macrophages. To some extent, blocking CD47/SIRPɑ signal is more promising than blocking PD-1/PD-L1 signal, because compared with PD-L1, the high expression of CD47 in tumor cells is more promising. Extensive, which means that drugs that block CD47/SIRPɑ signaling may have a broader spectrum of tumor treatment in the future. Therefore, the research and development of new drugs for CD47/SIRPɑ has been regarded as the next "PD-1/PD-L1", which has triggered many domestic and foreign companies to follow up.
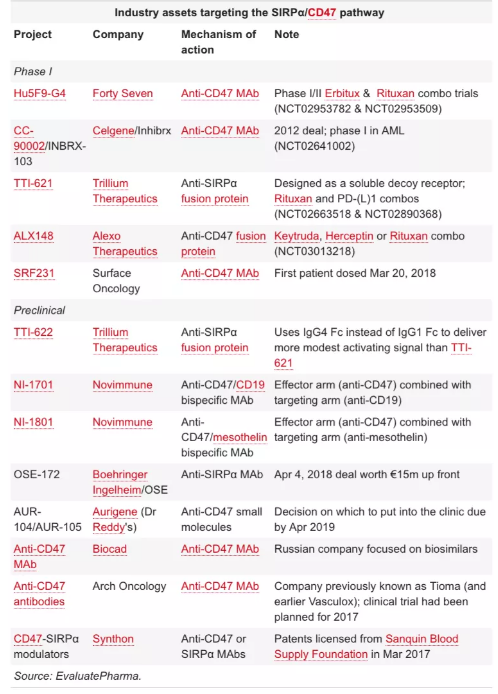
At present, the research and development of new drugs for this signaling pathway are mainly divided into three categories. The first category is CD47 blocking antibodies, and the second category is SIRPɑ blocking antibodies. Both types of antibodies block CD47 and SIRPɑ by binding to CD47 and SIRPɑ, respectively. The SIRPɑ interacts with each other to activate the phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages. The third type is the recombinantly expressed SIRPɑ FC protein. The principle of action is that on the one hand, the SIRPɑ recombinant protein competes with the SIRPɑ on the surface of the macrophage to bind to the tumor. CD47 on the surface inhibits the CD47/SIRPɑ signaling pathway, on the other hand, it plays an anti-tumor effect through the ADCC/ADCP effect mediated by Fc. (Table 1 shows some of the drugs under development for the CD47/SIRPɑ signaling pathway)
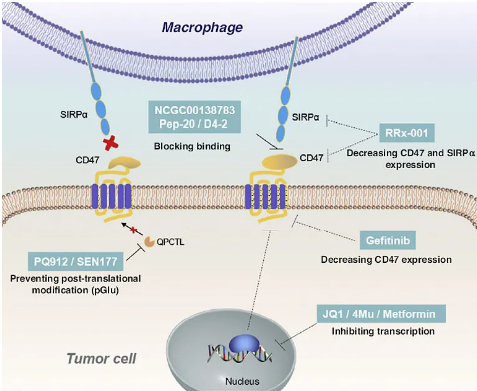
In addition, some small molecules for the CD47/SIRPɑ signaling pathway are also in the development process. Small molecules are mainly divided into two categories from the mechanism of action. One is directly binding to CD47, thereby blocking the CD47/SIRPa signal; the other The class is to down-regulate the expression of CD47/SIRPa signaling molecules by affecting transcription, translation or post-translational modification. (As shown below)
In response to the research and development of drugs for this hot tumor immune signaling pathway, Kebai Biosciences has developed a related cell screening model, which can be used for functional screening and measurement of macromolecular and small molecule drugs targeting this signaling pathway.
SIRPɑ Effector Reporter Cell RQP74122
CD47+ Target Cell Line RQP74124
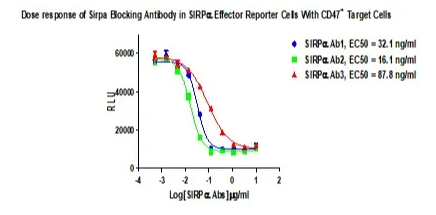
Figure 4. Dose response of Sirpɑ Blocking Antibody in SIRPɑ Effector Reporter Cells With CD47+ Target Cells.
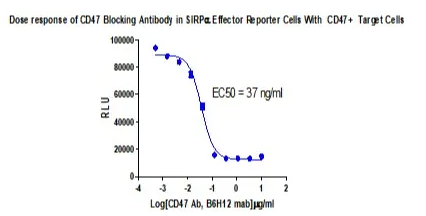
Figure 5. Dose response of CD47 Blocking Antibody in SIRPɑ Effector Reporter Cells With CD47+ Target Cells.
SIRPɑ/CD47 Dual Effector Reporter Cell RQP74123
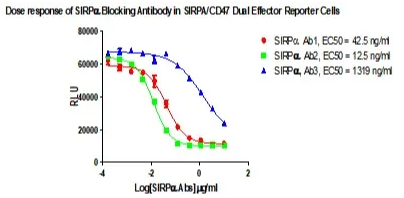
Figure 6. Dose response of SIRPa Bloking Atibody in SIRPɑ/CD47 Dual Effector Reporter Cells.
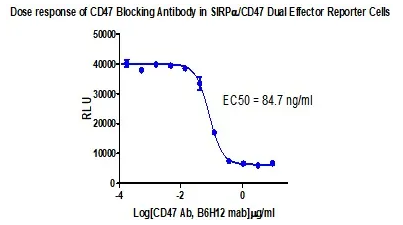
Figure 7. Dose response of CD47 Bloking Atibody in SIRPɑ/CD47 Dual Effector Reporter Cells.

