BRCA1/BRCA2 genetic testing standards
Breast cancer susceptibility genes (BRCA) are important tumor suppressor genes, including BRCA1 and BRCA2. BRCA1/2 gene is an important biomarker to assess the risk of breast cancer, ovarian cancer and other related cancers, and it is also a biomarker that affects the choice of individualized treatment options for patients. BRCA1/2 plays a key role in cellular DNA damage and repair pathways. Early studies have found that BRCA1/2 is the main cause of hereditary breast/ovarian cancer syndrome; recent studies have shown that BRCA1/2 mutations increase the risk of colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, skin cancer, and male prostate cancer.
Breast cancer women with BRCA1/2 gene mutations have a lifetime risk of breast cancer of 60%-85%, and the incidence is younger. Although most breast cancers are sporadic and only less than 5% of breast cancers are hereditary, more than 90% of them are related to BRCA1/2. Studies have reported that BRCA1/2 mutations are related to loss of estrogen receptor expression, larger tumors, and higher malignancy, which often indicate a later stage and a worse prognosis; similarly, it also increases the risk of male breast cancer.
Ovarian cancer women with BRCA1/2 gene mutations have a lifetime risk of ovarian cancer ranging from 26% to 54%, and the BRCA1 mutation rate is higher than BRCA2. BRCA1/2 mutations account for about 27% of familial ovarian cancers. The new ovarian cancer risk prediction model based on BRCA1/2 gene mutations and a clear family history is more accurate and can be used for ovarian cancer genetic counseling.
The BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes were discovered in the 1990s and are located on chromosomes 17 and 13, respectively. They are tumor suppressor genes and their protein products are involved in DNA repair and other processes. There are thousands of BRCA1/2 gene mutations that have been discovered, some of which are clearly pathogenic mutations. The incidence of BRCA1/2 pathogenic mutations in the population is about 0.1%-0.3%, and its incidence can reach 2.1% in Ashkenazi Jews, a high-risk race.
BRCA1/2 current drug indications
①Olaparib:
• After receiving chemotherapy (if hormone receptors are positive, then endocrine therapy), HER2-negative patients with metastatic breast cancer (MBC) with harmful germline mutations of BRCA1/2;
• As a maintenance treatment for patients with recurrent ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer or primary peritoneal cancer that are sensitive to platinum-based chemotherapy (complete response (CR) or partial response (PR));
• After third-line treatment, patients with ovarian cancer who carry BRCA1/2 harmful germline mutations.
②Niraparib:
• Maintenance treatment for ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer that recurred after CR or PR after platinum drug treatment, without the need to detect BRCA genotype.
③Rucaparib:
• As a maintenance treatment for patients with recurrent ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer or primary peritoneal cancer that are sensitive to platinum-based chemotherapy (complete response (CR) or partial response (PR)).
• After second-line treatment, ovarian cancer patients with BRCA1/2 harmful germline mutations.
We can provide diagnostic standards for BRCA1/2 multiple mutation types to ensure the detection limit, sensitivity and stability of the diagnostic method.
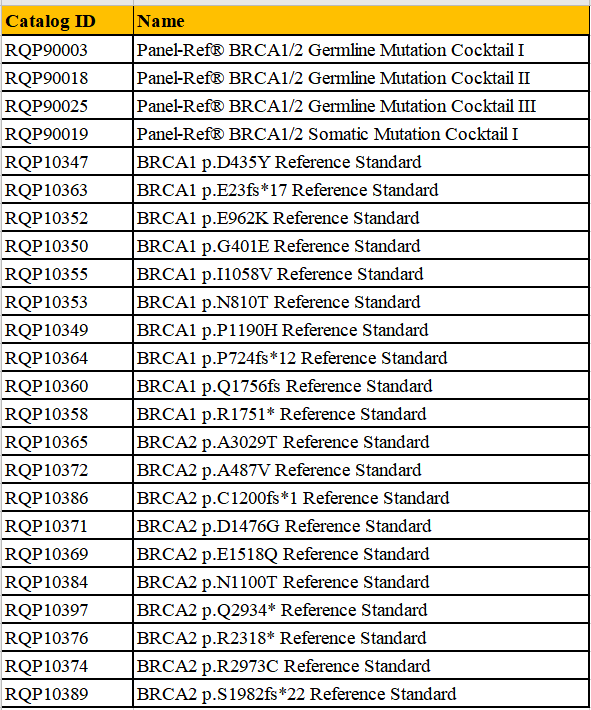
Part of product data
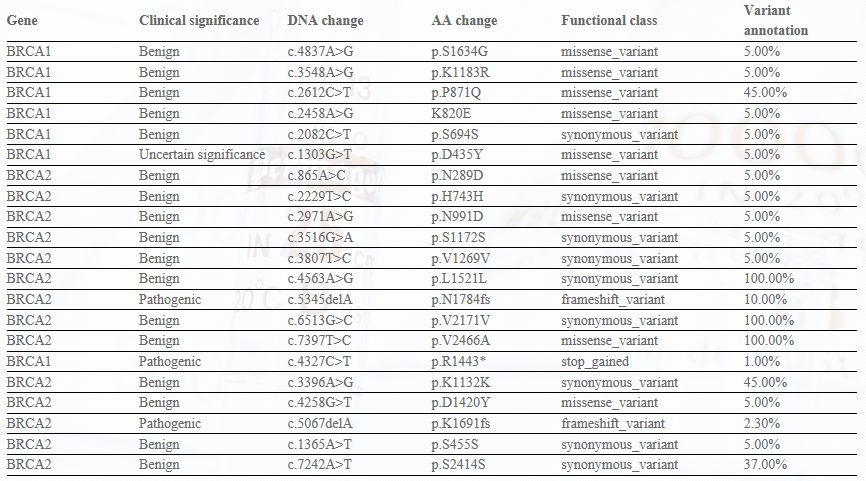
Panel-Ref® BRCA1/2 Germline Mutation Cocktail I RQP90003
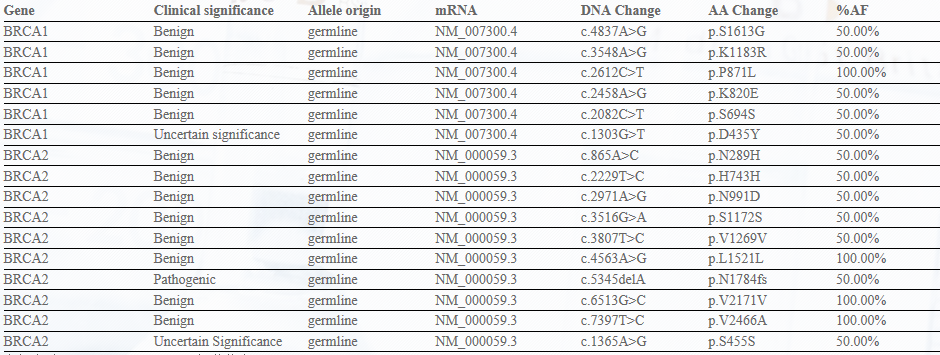
Panel-Ref® BRCA1/2 Germline Mutation Cocktail II RQP90018
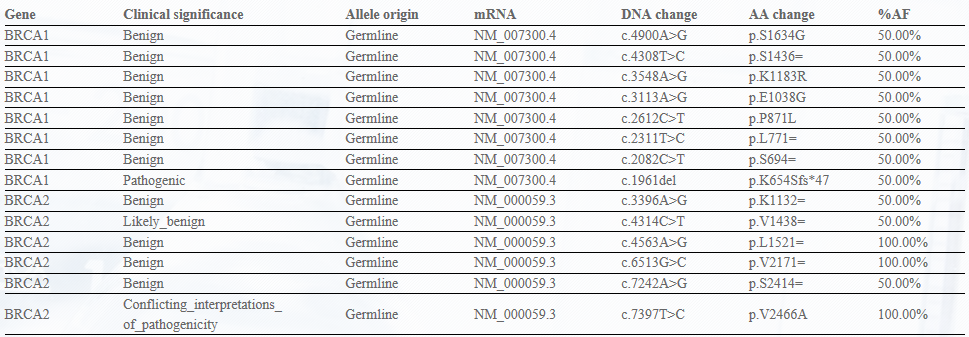
Panel-Ref® BRCA1/2 Germline Mutation Cocktail III RQP90025
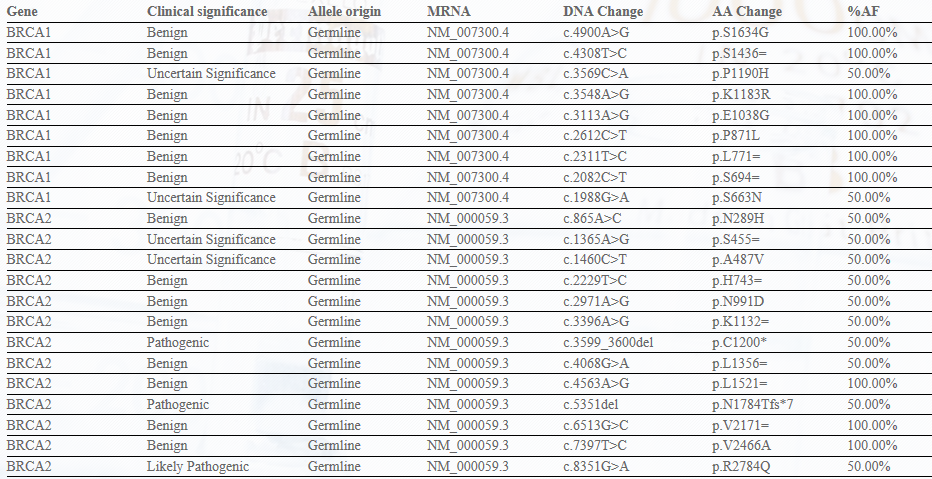
4
Panel-Ref® BRCA1/2 Somatic Mutation Cocktail I RQP90019